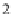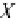Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
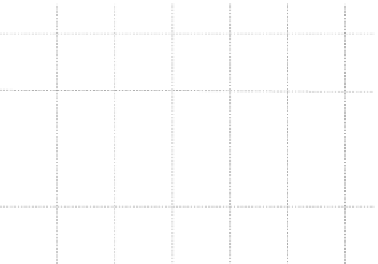
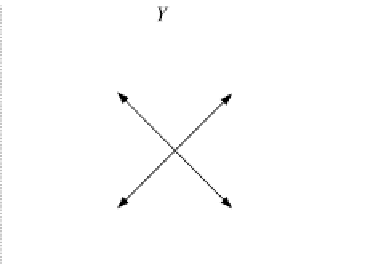
Fig. 3.2
Eight vectors whose
coordinates are shown in
Table
3.1
Ta b l e 3 . 1
Values associated
with the eight vectors in
Fig.
3.2
x
h
y
h
x
t
y
t
x
y
|
vector
|
2
0
0
0
2
0
2
0
2
0
0
0
2
2
−
2
0
0
0
−
2
0
2
0
−
2
0
0
0
−
2
2
√
2
1
1
0
0
1
1
√
2
−
1
1
0
0
−
1
1
√
2
−
1
−
1
0
0
−
1
−
1
√
2
1
−
1
0
0
1
−
1
3.5 3D Vectors
A 3D vector simply requires an extra component to represent its
z
-component
z
:
=
x
z
T
r
y
and its length is given by
x
+
y
+
z
.
|
r
|=
3.6 Vector Manipulation
Vectors are very different to scalars, and rules have been developed to control how
the two mathematical entities interact with one another. For instance, we need to
consider vector addition, subtraction and multiplication, and how a vector is modi-
fied by a scalar. Let's begin with multiplying a vector by a scalar.