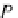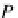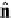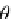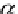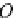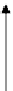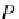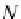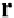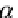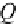Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
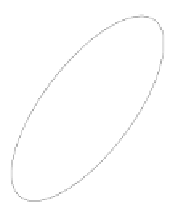
Fig. 9.11
Aviewofthe
geometry associated with
rotating a point about an
arbitrary axis
Fig. 9.12
A cross-section
and plan view of the
geometry associated with
rotating a point about an
arbitrary axis
•
P(x
p
,y
p
z
p
)
is the point to be rotated by angle
α
to
P
(x
p
,y
p
,z
p
)
.
•
O
is the origin, whilst
p
and
p
are position vectors for
P
and
P
respectively.
From Fig.
9.11
and Fig.
9.12
:
p
=
−−
ON
+
−−
QP
.
+
−−
NQ
To find
−−
ON
:
|
n
|=|
p
|
cos
θ
= ˆ
n
·
p
therefore,
−−
ON
=
n
= ˆ
n
(
n
ˆ
·
p
).
To find
−−
NQ
:
NQ
NP
r
NQ
NP
−−
NQ
=
=
r
=
cos
α
r
but
p
=
n
+
r
= ˆ
n
(
n
ˆ
·
p
)
+
r
therefore,
r
=
p
− ˆ
n
(
n
ˆ
·
p
)