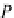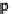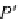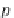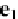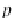Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
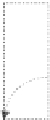
Fig. 7.3
Translate a point by
(t
x
,t
y
)
T
. The position vector
p
points to the translated point
P
=[
t
y
]
where
t
t
x
with
components:
t
x
)
e
1
+
y
t
y
e
2
p
=
(x
+
+
and agrees with the translation matrix
⎡
⎤
⎡
⎤
⎡
⎤
x
y
1
10
t
x
01
t
y
00 1
x
y
1
⎣
⎦
=
⎣
⎦
⎣
⎦
.
7.5.2 Rotational Qualities of the Unit Bivector
We know from Chap. 2 that multiplying a complex number by imaginary
i
rotates
that complex number by 90°. In geometric algebra the 2D pseudoscalar
e
12
is also
imaginary in that
e
12
=−
1, and has similar rotational properties, but has the extra
feature of controlling the direction of rotation. For example, Fig.
7.4
shows
pe
12
which rotates
p
, 90°:
p
=
p
1
e
1
+
p
2
e
2
pe
12
=
(p
1
e
1
+
p
2
e
2
)
e
12
=
p
2
e
1
=−
p
2
e
1
+
p
1
e
2
.
p
1
e
2
−
Fig. 7.4
pe
12
rotates
p
, 90°