Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
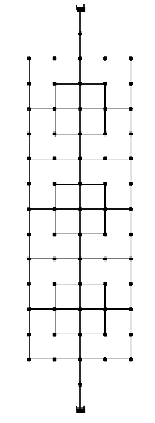
Figure 4.2
Network matrix represented by binary code (according to Möderl et al.,2007)
Figure 4.3
Typical layouts of MDS network sample (Möderl et al.,2007)
The problem of network generation is also known in the field of river and drainage/sewer
networks as well as in the wider context in mathematics and computer science. In their
further research, Möderl et al. (2009) propose a MATLAB tool called
Case Study Generator
(CSG) that creates virtual urban drainage networks. Having the features of random generation
of nodal coordinates and elevations, and preventing the link intersection, CSG brings the
network configuration closer to the reality. A sample of 10,000 synthetic networks has been
generated and analysed for hydraulic performance under surface flooding.
A few other applications related to drainage networks can be found for instance in the work
of Ghosh et al. (2006) who developed a program named
Artificial Network Generator
(ANGel). This is an ArcGIS tool that can develop fractal trees for reference network or line
and is able to assess travelling time distribution and does various hydrological statistics for
generated layouts. Furthermore, Sitzenfrei et al. (2010) present
Virtual Infrastructure
Benchmarking
(VIBe) as methodology for algorithmic generation of
Virtual Case Studies
(VCSs) especially for urban water systems. VIBe provides input files for EPANET and
SWMM software using parameters based on real world case studies and literature. The
generated sample of 1000 VCSs was simulated and evaluated in this study.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search