Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0.9
0.8
PBI50
PBI151
PBI200
NPI50
NPI151
NPI200
NRT50(w)
NRT151(w)
NRT200(w)
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0.92
0.93
0.94
0.95
0.96
0.97
0.98
0.99
1
ADFavg
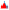
Figure 7.6
Reliability measures for networks ngt 01-50, 01-151 and 01-200 for demand growth of 32%
Figure 7.4 shows two networks with GA optimised pipe diameters supplying the same total
demand. Again, the network
O20sn80
is more reliable but in this case has rather similar
buffer compared to
O20sn73
. Although optimised for lower total demand, the network
O20sn73
is less reliable than
sn73
, as well as is the case with
O20sn80
and
sn80
, which can
be seen by comparing the results in Figures 7.3 and 7.4.
Figure 7.5 shows also that the better connected networks,
sn0199
and
sn0109
, are more
reliable than
sn0179
. These two perform within similar
ADF
avg
range despite the fact that
sn0199
supplies more than twice the demand of
sn0109
. This is possible as this network is
the only of the three that is connected with two pipes to the source. Nonetheless, the higher
demand results in the lower
PBI
and
NRT
values, also compared to
sn0179
.
Although kept with fixed diameters of 100 mm only, the geometry of the networks
ngt
01-50
,
01-151
and
01-200
, shows more realistic values of
NRT
, in the range of 9 to 37 hours. In
Figure 7.6, these values have been expressed in weeks, to maintain the same scale of the Y-
axis as in the previous three diagrams. Like in the case of three
sn01
networks, the better
connected networks,
ngt01-151
and
ngt01-200
, are more reliable than
ngt01-50
. Equally,
these two networks have the similar
ADF
avg
range because the bigger one,
ngt01-200
, also
supplies the higher demand than
ngt01-151
. Consequently, the smaller network has a bit
more buffer expressed in the difference between the values for
NPI
and
NRT
. The higher
NPI
value of
ngt01-50
compared to the other two is due to lower nodal elevations.
The similar trend can be observed analysing the
PBI
values. The two bigger networks show
similar values and more favourable range of
ADG
avg
than the smallest one. The difference in
the
PBI
values is however much smaller than in case of
NPI
and
NRT
, likely resulting from
central positions of the source i.e. the lower level of friction losses. Last but not the least, the
generally higher values of
ADG
avg
observed in case of the three
ngt
networks are also caused
by good connectivity of the source. Hence, the preliminary analysis of all the figures
confirms the correlations that can be summarised in the following bullets:
-
Demand increase of a network causes higher friction losses (i.e. the lower nodal
pressures/demands) leading to lower values of
ADF
avg
,
PBI
,
NPI
and
NRT
.
-
At the same level of demand, better connected networks will have more favourable range
of
ADF
avg
.


































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search