Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Like in Figure 4.4a, the network in Figure 4.7 is a complete- and simple graph with total 12
connections out of six links, and the node degree ranging between one and three.
Nodes in water distribution networks are rarely connected with more than four pipes. Having
a restriction on the maximum node degree can therefore drastically reduce the number of
non-zero matrix elements, which limits the number of combinations and makes the network
generation more efficient. Having this in mind, the algorithm has been developed with the
limitation that each node can be connected to a maximum of three additional nodes, in the
process of network generation. The choice for one, two or three closest connections will
obviously influence the complexity of generated networks. Eventually, the actual nodal
degree will occasionally exceed three, which can be further maximised in the settings of the
programme. In how many cases and where in the network this will happen, depends in
general on the ratio between the selected number of nodes and links, and in particular on the
order of nodes in the process of generation and their coordinates, which is for larger sets not
easy to predict in advance. Next to easier manipulation of matrices, this somewhat erratic
generation process is believed to offer more variety of network layouts. Applying no
limitation, the absolute maximum of nodal connections will rarely exceed six.
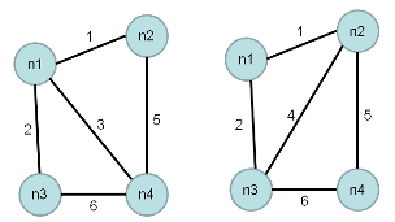
The planarization is applied in the next step of network generation, where all created pipe
crossings are eliminated. The separation of edges that cross each other will be done by
constructing two sub-graphs each with one of the edges, as shown in Figure 4.8. The result in
the corresponding matrices is the change of one single element, as done in Table 4.7.
Figure 4.8
Spanning sub-graphs of network in Figure 4.7
Table 4.7
Upper triangular matrix of spanning sub-graphs in Figure 4.7
From node
To node
From node
To node
n1
n2
n3
n4
n1
n2
n3
n4
n1
0
1
2
3
n1
0
1
2
0
n2
0
0
5
n2
0
4
5
n3
0
6
n3
0
6
n4
0
n4
0
There are several methods of creating planar graphs known in the literature such as,
Path
Addition Method
of Hopcroft and Tarjan (1974),
Tree Data Structure Method
developed by
Booth and Lueker (1976), and more recently developed
Edge Addition Method
of de






Search WWH ::

Custom Search