Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
each software has associated operating system or hardware dependancy require-
ments. Moreover, tight delivery deadline requirement may necessitated the use
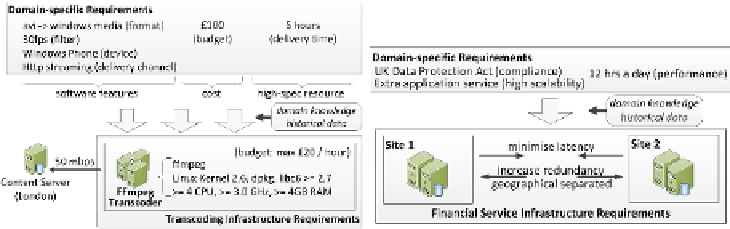
of high-cpu resources. Figure 6 illustrates how the transcoding requirements are
translated into infrastructure requirements.
Examples of the ontology relationships between domain-specific and infras-
tructure layer for the media transcoding application are given as follow:
Format ,
codec, device, processing filters
and
delivery channel
isDependOn
soft-
ware stack
which indicates the transcoding software's capabilities or features;
delivery time
isDependOn
network latency
,
bandwidth
and
hardware
capability
as it requires fast bandwidth and high cpu for fast processing.
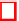
For the financial services example, the UK Data Protection Act regulatory
requirement indicates that the infrastructure resources being provisioned must
be located within UK. Two identical mirror infrastructure must be provisioned
at different geographical location in order to meet the high availability and high
disaster recovery requirements. High bandwidth usage is required as the appli-
cation service needs to utilise stock market values. The demand of high response
time requires high-cpu and high-memory resources for faster computation. The
formulation of such requirements are illustrated in Figure 7.
Examples of the ontology relationships for the financial services application
are given below:
Compliance
isDependOn
geographical
because a 'UK Data
Protection Act' indicates that no data can be processed outside the UK bound-
ary;
data
isDependOn
software stack
as it requires third party verification
services;
high availability
and
high scalability
are complex requirements
and depend on how infrastructure resources are provisioned. The concepts of
infrastructure
,
site
,
resource group
and
resource
are used to indicate that
different geographical sites must be provisioned, and each site
hasRequirement
latency
,
bandwidth
and
geographical
.
The middle layer of the proposed model serves as an agent that translate the
domain-specific ontology onto related infrastructure requirements ontology. This
provides an abstract view of high-level requirements from the application's per-
spective. Infrastructure requirements ontology can then be mapped to resource
ontology using ontology query language [5].
Fig. 6.
Media transcoding application
Fig. 7.
Financial services application