Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
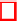
Fig. 2. Case Study 1:(a) Total energy consumption by data centers (b) Number of VM
migrations from DC1 to DC2 for the FAP mechanism (c) Execution time of tasks
that this increase in the execution time is very low and it is compensated by the
reduction in the power consumption (Figure 2).
In the second scenario, we consider two users, with distinct SLAs and each
user makes 400 task execution requests to a different data center (DC1 and
DC2). Our goal is to observe the rate of SLA violation when the workload of
both Data Centers is high (Figures 3 (a), (b), (c) and (d)).
In Figure 3(a), we can see that, even in a scenario with overloaded Data
Centers, our mechanism is able to maintain the power consumption below the
threshold (3 kWh) for each Data Center. With the CPU utilization threshold
of 80%, the power consumption decreased from 9
.
13 kWh to 5
.
65 kWh (DC1 +
DC2), reaching 38
.
2% of reduction in power consumption.
The number of SLA violations with two overloaded Data Centers was lower
than the one obtained with one overloaded Data Center (DC1) (Figure 3(d)).
With the CPU utilization threshold of 80%, the SLA violation decreased from
43
.
94% (DC1) to 31
.
48% (DC1 + DC2), reaching 12
.
46% of reduction in SLA
violations. This shows the appropriateness of VM migrations between different
Data Centers in an overloaded scenario.
6 Related Work
Table 1 summarizes the main characteristics of 6 papers that propose server
consolidation strategies for distributed environments.
As can be seen in this Table, three approaches [4, 6, 5] use multi-agent systems
to reduce power consumption and costs. One of them is targeted to Clouds and