Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
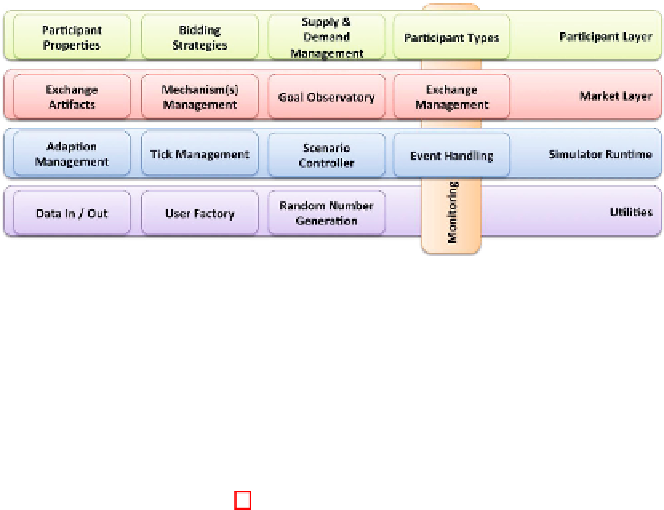
Fig. 1.
Conceptual Framework of a Simulation Environment for Autonomic Markets
5 Conceptualisation of a Simulator for Autonomic
Markets
Based upon our experiences with GridSim, we realised that trying to simulate
different aspects for the study of autonomic markets needs a more flexible sim-
ulation approach. In Section 3, we discussed some alternatives to GridSim, but
failed to see the ability to capture all aspects that we feel are necessary without
significant effort in the extension of an approach. In this section, we propose
a conceptual architecture for an autonomic market simulator that will act as
a testing environment for the future studies. Fig. 1 illustrates the layers and
components of our proposed simulation architecture, which are as follows:
The
Monitoring Framework
captures key information on the market plat-
form through links to the Participant, Market and Simulator layers, and makes
this information available to the components that require it (e.g. the Goal Ob-
servatory). Monitoring information here captures the state of: mechanisms, the
market in general and the computational infrastructure, as described in [6].
The
Participant Layer
captures the aspects necessary to represent mar-
ketparticipantsaswellastheirvariousnuances and differentiating factors. The
key component is
participant type
, which identifies whether a participant is a
consumer, provider, prosumer, or broker. It also enables different participant
flavours like market makers, speculators, monopolists, aggressive and passive
participants. In accordance to the typical market simulators, we define
bidding
strategies
, as well as the management of
supply and demand
.Weusetheword
“management” to illustrate that this is not a statically defined process, but
entails stochastic and dynamic behaviours such as participants joining or leav-
ing the market, as well changes in their individual properties and requirements
over time.
Participant properties
capture additional information needed for each
participant type, e.g. range of wealth, resource types offered/desired, etc.
The
Market Layer
defines the components to implement an electronic mar-
ket. This includes: the
artefacts
to be traded, including their type, quantity
and period of availability or desirability; different allocation
mechanisms
like
the English or Continuous Double Auction, but also the means to create