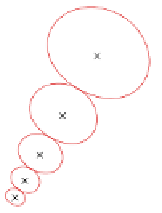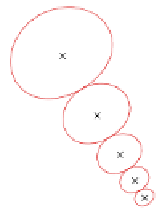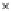Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 10.21. A Gabor filter set in the Fourier domain and the Fourier transforms of two linearly
symmetric images, overlayed. The
dashed
and
solid
axes represent the spectral energy con-
centrations of the two linearly symmetric images having gradient directions of 30
◦
and 45
◦
direction, respectively
an unnecessarily rough quantization of
the direction
because when the linear sym-
metry axis direction falls between two filter directions, two directions will signal a
presence of significant response power in their respective directions (Fig. 10.23). In
consequence, choosing the maximum power direction will not give better direction
resolution than the direction resolution in the Gabor filter tunings. Below, by using
direction tensors, we show that the limitation of the direction resolution attributable
to the filter tuning resolution can be reduced significantly by utilizing the structure
tensor theory.
Let the coordinates of the filter tune-on frequencies, marked by
×
in the example
of Fig. 10.21, be given as complex numbers:
z
kl
=
x
kl
+
iy
kl
(10.83)
The indices
k, l
, running over all filters in the Gabor filter set, represent the direc-
tion and the absolute frequency of the filter tunings. Then the second-order complex
moments of the discrete power spectrum are given by:
I
20
=
k,l
2
=
k,l
z
kl
(
z
kl
)
2
F
{k,l}
|
z
kl
|
F
{k,l}
|
2
|
(10.84)
and