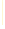Java Reference
In-Depth Information
54
ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator();
55
56
while
(
iterator.hasNext()
)
57
{
58
String color = iterator.next();
// get item
iterator.set(color.toUpperCase());
// convert to upper case
59
60
}
61
}
62
63
// obtain sublist and use clear method to delete sublist items
64
private static void
removeItems(
List<String> list
,
65
int
start,
int
end)
66
{
67
list.subList(start, end).clear();
// remove items
68
}
69
70
// print reversed list
71
private static void
printReversedList(
List<String> list
)
72
{
73
ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator(list.size());
74
75
System.out.printf(
"%nReversed List:%n"
);
76
77
// print list in reverse order
78
while
(
iterator.hasPrevious()
iterator.previous()
)
79
System.out.printf(
"%s "
,
);
80
}
81
}
// end class ListTest
list:
black yellow green blue violet silver gold white brown blue gray silver
list:
BLACK YELLOW GREEN BLUE VIOLET SILVER GOLD WHITE BROWN BLUE GRAY SILVER
Deleting elements 4 to 6...
list:
BLACK YELLOW GREEN BLUE WHITE BROWN BLUE GRAY SILVER
Reversed List:
SILVER GRAY BLUE BROWN WHITE BLUE GREEN YELLOW BLACK
Fig. 16.3
|
List
s,
LinkedList
s and
ListIterator
s. (Part 2 of 2.)
Lines 14 and 22 create
LinkedList
s
list1
and
list2
of type
String
.
LinkedList
is
a generic class that has one type parameter for which we specify the type argument
String
in this example. Lines 16-17 and 24-25 call
List
method
add
to
append
elements from
arrays
colors
and
colors2
to the
ends
of
list1
and
list2
, respectively.
Line 27 calls
List
method
addAll
to
append all elements
of
list2
to the end of
list1
.
Line 28 sets
list2
to
null
, because
list2
is no longer needed. Line 29 calls method
printList
(lines 41-49) to output
list1
's contents. Line 31 calls method
convertToUppercaseStrings
(lines 52-61) to convert each
String
element to uppercase,
then line 32 calls
printList
again to display the modified
String
s. Line 35 calls method