Java Reference
In-Depth Information
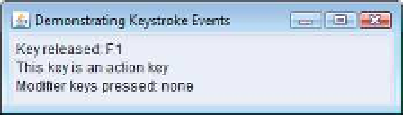
Fig. 12.37
|
Testing
KeyDemoFrame
. (Part 2 of 2.)
At line 25, the constructor adds the
JTextArea
textArea
(where the application's
output is displayed) to the
JFrame
. A
JTextArea
is a
multiline area
in which you can dis-
play text. (We discuss
JTextArea
s in more detail in Section 12.20.) Notice in the screen
captures that
textArea
occupies the
entire window
. This is due to the
JFrame
's default
BorderLayout
(discussed in Section 12.18.2 and demonstrated in Fig. 12.41). When a
single
Component
is added to a
BorderLayout
, the
Component
occupies the
entire
Con-
tainer
. Line 23 disables the
JTextArea
so the user cannot type in it. This causes the text
in the
JTextArea
to become gray. Line 24 uses method
setDisabledTextColor
to change
the text color in the
JTextArea
to black for readability.
Methods
keyPressed
(lines 31-37) and
keyReleased
(lines 40-46) use
KeyEvent
method
getKeyCode
to get the
virtual key code
of the pressed key. Class
KeyEvent
con-
tains virtual key-code constants that represent every key on the keyboard. These constants
can be compared with
getKeyCode
's return value to test for individual keys on the key-
board. The value returned by
getKeyCode
is passed to
static
KeyEvent
method
getKey-
Text
, which returns a string containing the name of the key that was pressed. For a
complete list of virtual key constants, see the online documentation for class
KeyEvent
(package
java.awt.event
). Method
keyTyped
(lines 49-54) uses
KeyEvent
method
get-
KeyChar
(which returns a
char
) to get the Unicode value of the character typed.
All three event-handling methods finish by calling method
setLines2and3
(lines 57-
69) and passing it the
KeyEvent
object. This method uses
KeyEvent
method
isActionKey
(line 60) to determine whether the key in the event was an action key. Also,
InputEvent
method
getModifiers
is called (line 62) to determine whether any modifier keys (such as
Shift
,
Alt
and
Ctrl
) were pressed when the key event occurred. The result of this method
is passed to
static
KeyEvent
method
getKeyModifiersText
, which produces a
String
containing the names of the pressed modifier keys.
[
Note:
If you need to test for a specific key on the keyboard, class
KeyEvent
provides
a
key constant
for each one. These constants can be used from the key event handlers to
determine whether a particular key was pressed. Also, to determine whether the
Alt
,
Ctrl
,
Meta
and
Shift
keys are pressed individually,
InputEvent
methods
isAltDown
,
isCon-
trolDown
,
isMetaDown
and
isShiftDown
each return a
boolean
indicating whether the
particular key was pressed during the key event.]
Layout managers
arrange
GUI components in a container for presentation purposes. You
can use the layout managers for basic layout capabilities instead of determining every GUI
component's exact position and size. This functionality enables you to concentrate on the
basic look-and-feel and lets the layout managers process most of the layout details. All lay-
out managers implement the interface
LayoutManager
(in package
java.awt
). Class
Con-