Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
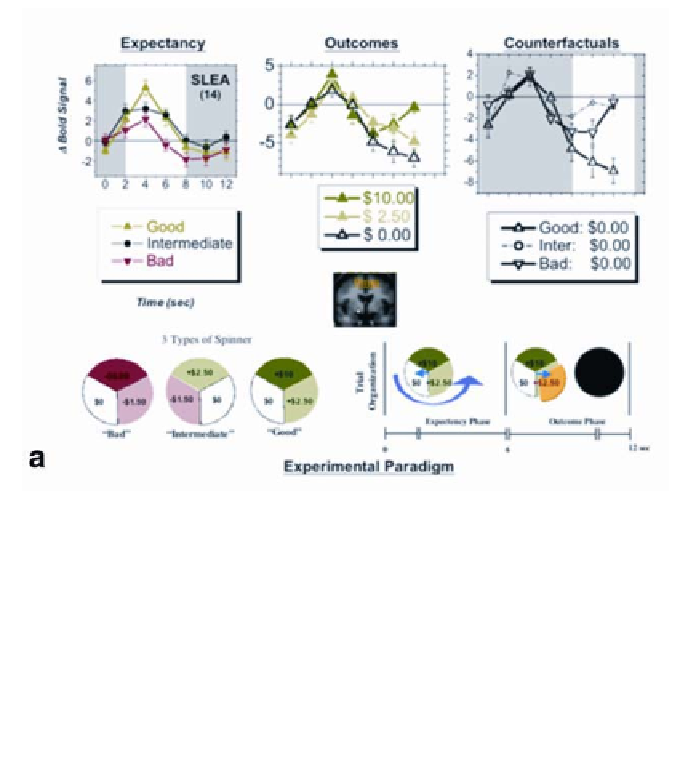
Figure 7a
. An experimental design that applies the principles of prospect theory and decision affect theory
(figure adapted with permission from (32,38)) utilizing three spinners in a game of chance. Organized as a
series of single trials, the trial sequence started with presentation of one of these spinners, and continued with
an arrow rotating on it. After six seconds, this rotating arrow would abruptly stop and the sector upon which it
had landed would flash for 5.5 seconds, showing that the subject had won or lost that amount of money. With
three spinners, each with three outcomes, this experiment asked which reward/aversion regions in the brain
would process differential expectancy and/or outcome effects. With one outcome ($0) shared across spinners,
it could explicitly also evaluate counterfactual comparison effects (171,170). The graphs at top display differ-
ential expectancy effects (left), differential outcome effects (middle), and counterfactual comparisons (right)
from a region of signal change in the sublenticular extended amygdala (SLEA). The
x
-axis displays time in
seconds, while the
y
-axis displays normalized the fMRI signal.
theory as well as Mellor's decision affect theory (131,170,171,254). Its results
temporally segregated expectancy effects from outcomes in a number of reward
regions (Figure 7a), and observed rank ordering of signal responses in a set of
brain reward regions that reflected the differential expectancy conditions. Rank
ordering of fMRI signal responses to differential monetary outcomes was also
observed. Strong effects of expectancy on subsequent outcomes, or counterfac-
tual comparisons (170,171), were measured for an outcome shared across expec-
tancy conditions. The observation of effects from counterfactual comparisons is
a fundamental experimental control supporting the reliability of the expectancy
measures. At the high spatial resolution of this 3T fMRI study, some reward
regions were activated solely by expectancy or outcome effects. Intriguingly, a
few regions were involved with multiple functions and processed differential
expectancies, outcomes, and counterfactual comparisons. Later studies using