Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
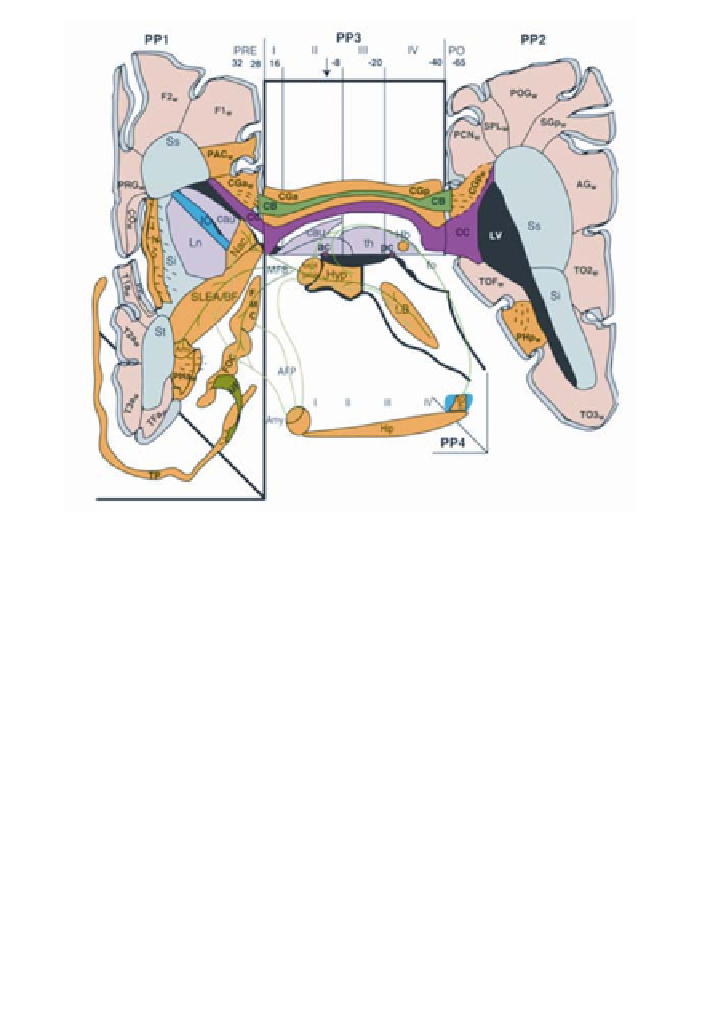
Figure 5
. Diagrammatic representation of topologic relationships of brain stem and parcellated forebrain
structures (158). Limbic and paralimbic structures (in yellow) and some of their main connections are shown
in a schematic fashion. The diagram is flanked on the left and right by coronal projection planes (PP1, PP2).
The paracallosal coronal slabs I-IV are distinguished by verticals in the interval, displayed on the midsagittal
plane (PP3) of the hemisphere. The numbers aligned along the top of this plane correspond to the
y
-axis
(anterior-posterior) coordinates of the Talairach stereotactic system (246) for the standard brain used to de-
velop this system. PP1 corresponds to a composite coronal plane (temporal lobe is forced to be more anteri-
orly located) projected at the Talairach coordinate, indicated by the vertical black arrow in paracallosal slab II.
PP2 corresponds to the immediately posterior callosal coronal plane at Talairach coordinate -40. The projec-
tion of these slabs within the temporal lobe is indicated by step PP4. Whereas the amygdalo-hippocampal
junction will have the approximate lateral projection of PP4, the hippocampus and fornix will actually curve
medially and approximate the plane of PP3. Its representation in PP4 is a schematic emphasis of the anterior-
posterior projection of the structure. The decussation of anterior (ac) and posterior (pc) commissures is indi-
cated by brown squares at PP3/II and IV respectively. Ventricular system (LV) (black) is projected topologi-
cally within the 3-dimensional representation. Cortex: neocortex (gray), limbic cortex (yellow). nuclei:
thalamus (th), caudate (cau), putamen-pallidum (Ln), amygdala (amy) (pink). White matter: radiata (beige);
corpus callosum (cc) (red); internal capsule (IC). Cortical paralimbic structures: parahippocampal gyrus (PH);
temporal pole (TP); frontoorbital cortex (FOC); frontomedial cortex (FMC). Gray limbic structures: limbic
brain stem (LB); hypothalamus (Hyp); hippocampus (Hip); amygdala (Amy); septal area (sept); preoptic area
(proa); nucleus accumbens septi (NAc); sublenticular extended amygdala and basal forebrain (SLEA/BF);
insula (INS); habenula (Hb). Abbreviations: White matter: superior sagittal stratum (Ss), inferior sagittal
stratum (Si), temporal sagittal stratum (St). Limbic fascicles shown in this figure: uncinate fasciculus (UF);
cingulum bundle (CB); dorsal hippocampal commissure (dhc), fornix (fo), fimbria (fi); medial forebrain
bundle (MFB); amygdalofugal projection (AFP).
Some of the first neuroimaging studies to identify neural activity in a subset
of these brain regions during the processing of rewarding stimuli used monetary
or drug rewards (23,37,250). In the double-blind cocaine vs. saline infusion