Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
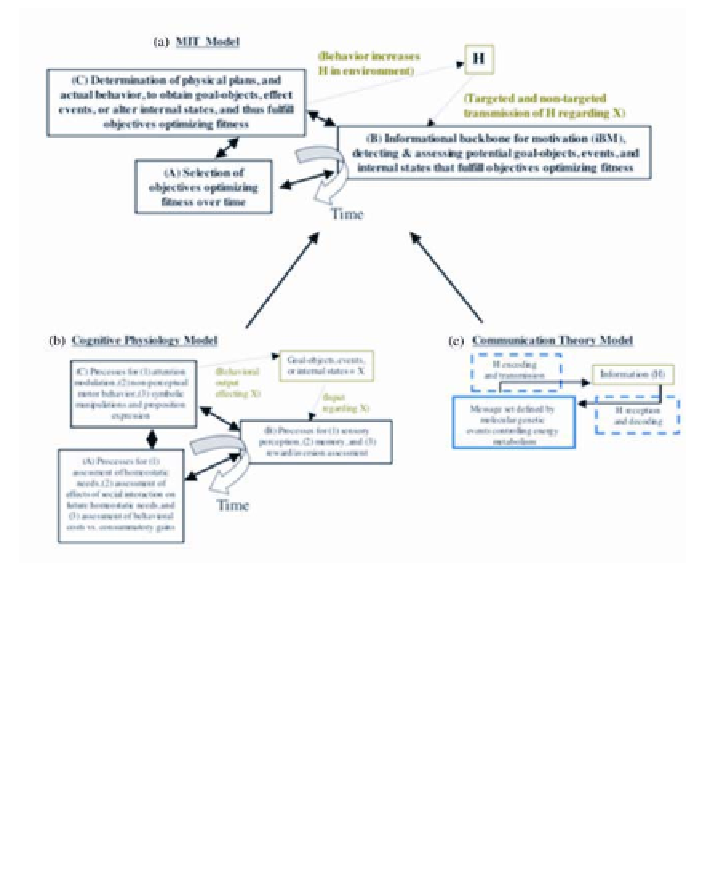
Figure 2
. (
a
) The MIT (Motivation Information Theoretic) Model synthesizes the processes of (B) with those
of (C) with input entry via an informational backbone for motivation (iBM). This information backbone
assesses if potential goal-objects will fulfill organism objectives for fitness, and interfaces with the behavioral
operation to obtain such goal-objects. Given the interdependence of these sets of brain processes on each
other, they function as if they were all orthogonal to time. See text for further details. (
b
) A cognitive physiol-
ogy model organized around three general operations for mediating directed action. One operation (A) is
composed of processes that evaluate organism needs across multiple dimensions, and potential energy costs
for fulfilling these needs by plans devised in (C). A second operation (B) includes processes for sensory
perception, memory of previous outcomes and their contexts, and assessment of how rewarding or aversive
potential goal-objects or events might be. (
c
) Information (H), as defined by Shannon and Weaver (234), is
received and decoded during communication by processes that allow incoming information to be linked to the
set of communicable messages. Messages, in turn, are encoded and transmitted in the form of behavior. Self-
organizing organisms always generate entropy as an outcome, which acts as a force behind the development
of complexity in coding/decoding systems such as the brain, and their evolution toward greater complexity
(204). See text for definitions of abbreviations.
intricate feedback loops in their production of a behavioral trajectory, they are
not necessarily sequential but orthogonal to time. The third operation, in hu-
mans, clusters a number of possible actions: (1) modulation of attention-based
filtering of perceptual input, (2) organization of motor output to obtain goal-
objects, (3) control of cognitive, logical, and internal imagery systems (and their
symbolic output in the form of language) to increase the range of goal-objects
that can be obtained, problems that can be solved, or events that can be experi-
enced (139,177,238).