Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
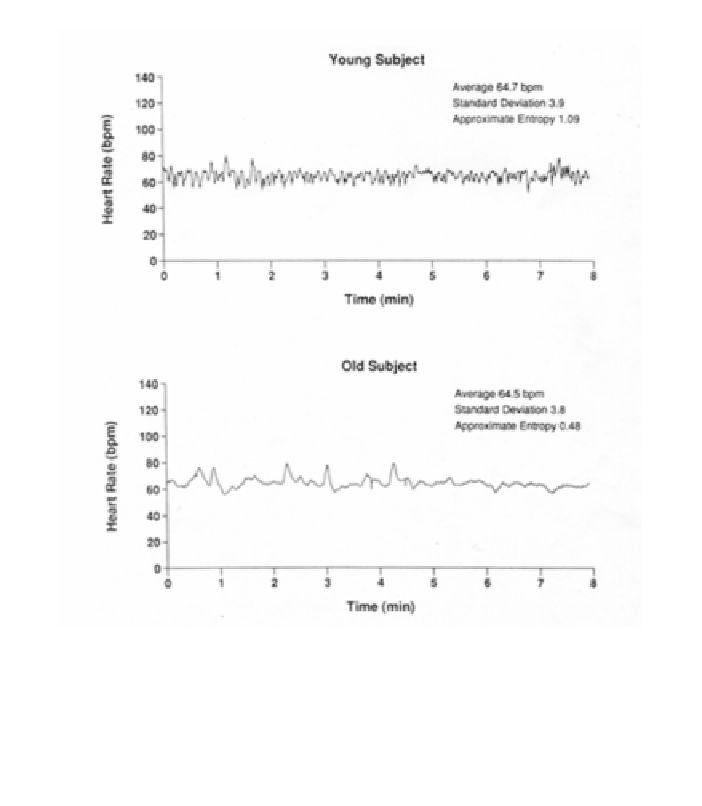
Figure 2
. Continuous heart rate time series over 8 minutes for a healthy young subject (top
graph) and a healthy elderly subject (bottom graph). Note the similar average heart rate and
standard deviation of heart rate, but different dynamics as quantified by Approximate Entropy.
Reprinted with permission from (5).
respiratory tree (7) or smaller and smaller vessels in the circulatory system (8)
look similar whether they are measured in microns, millimeters, centimeters, or
meters. In fact, the smaller the measuring device, the larger the length of a frac-
tal object. This property is known as "power-law scaling" because a smaller
measuring device leads to an exponential (i.e., "the power") increase in the
length of a fractal object. The output of dynamic physiologic processes such as
heart rate, measured over time rather than space, also have fractal properties (9).
Their oscillations appear self-similar when observed over seconds, minutes,
hours, or days. Furthermore, they demonstrate power-law scaling in the sense
that with a smaller frequency of oscillation of these signals their amplitude in-
creases exponentially.