Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
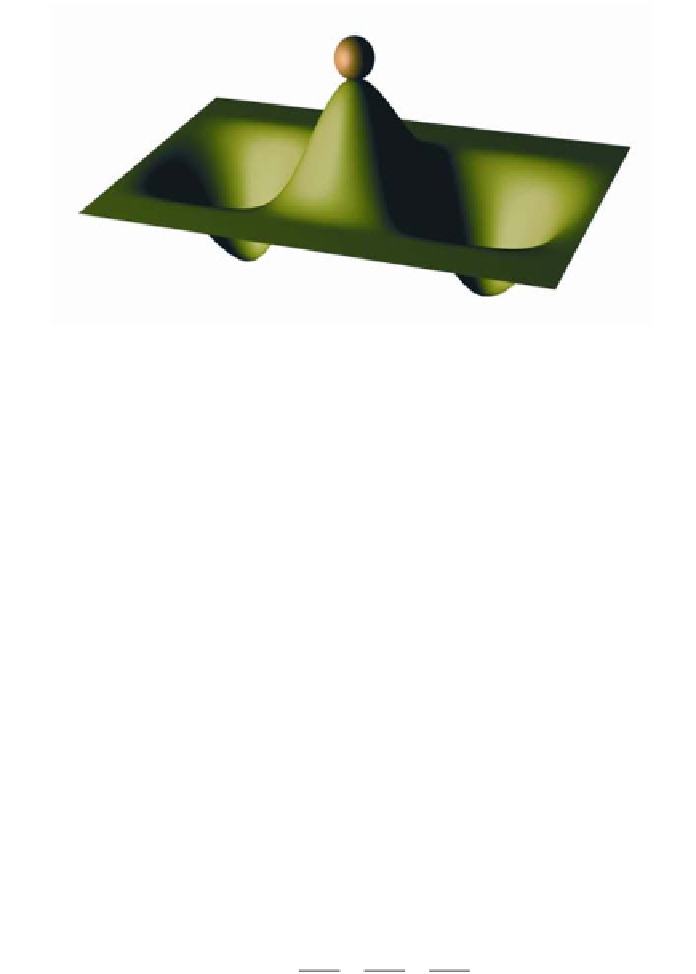
Figure 2
. Symmetry breaking. This is a mechanical analogure of the pattern presented in Fig-
ure 1. The initial state of the system (the initial population sizes of the two competing cell
populations) is represented by the ball at the top. Any small initial difference will be amplified,
and eventually the ball will end up in one of the two minima. The initial symmetry is broken
and one of the possible exclusion points has been chosen.
4.
COMPETITION WITH SPATIAL DYNAMICS
By introducing diffusion in the competing species (clones), simple models
can be generalized to spatially extended ones. The standard procedure is to add a
diffusion term to the Lotka-Volterra equation.
The new model now takes the form
¬
dN
N
-
B
N
=
rN
1
-
+
D
2
N
,
[9]
1
1
2
-
11
--
1
1
dt
K
®
1
¬
dN
N
-
C
N
=
rN
1
-
+
D
2
N
,
[10]
2
2
1
-
22
--
2
2
dt
K
®
2
where
D
i
/
2
N
i
are the diffusion terms for each clone. Each population spreads at a
rate
D
i
(the diffusion rate), and we have, in three dimensions,
2
2
2
s
NNN
s
s
2
N
=++
s
.
[11]
x
2
s
y
2
s
z
2
Gatenby and Gawlinsky (30) used a similar model to study tumor invasion. The
tumor host interface was treated as two competing cell populations in a low pH