Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
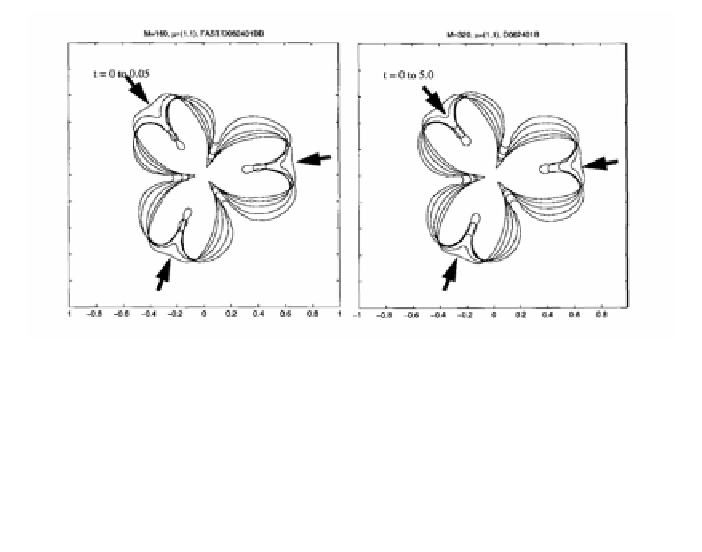
Figure 4
. Effect of G, relative force strength, on clefting of epithelial rudiment embedded in
mesenchyme or gel of the same viscosity. Arrows indicate the directions of imposed forces,
and also the direction of time sequence. Nondimensional surface tension C = 0.005, viscosity
ratio B = 1. (
a
) G = 160,
t/T
= 0 to 0.05; (
b
) G = 50,
t/T
= 0 to 5. A tripling of the relative cleft-
ing force G divides the nondimensional clefting time by a factor of approximately 100. The
weaker force leaves wider clefts (cf. Figure 6). Reprinted with permission from Lubkin and Li
(2002) (37).
enough (Figures 4-6). The nondimensional surface tension C significantly af-
fected the evolving shape. If C was very large, the preexisting clefts retreated
before the new cleft was fully formed, regardless of the relative clefting force G.
For fixed surface tension C, the shape depended only subtly on the viscosity ratio
and force parameters B and G.
The most significant differences between simulations were in the time
scales. When the nondimensional clefting force G was small, it took significantly
longer for clefts to form than at larger G values. In particular, decreasing the
clefting force by a factor of 3 increases the clefting time by a factor of about 100
(Figure 4).
Our most significant finding was that when the viscosity ratio B was high, it
took significantly longer for clefts to form than at lower B values. In particular,
increasing the viscosity of the mesenchyme/gel by a factor of 10 typically tripled
the time to form a cleft of a characteristic depth (Figure 4). This relates directly
to the question of what is going on in the mesenchyme-free experiments. Is the
branching that occurs in a salivary epithelium the same when its mesenchyme is
removed and replaced by a material which is much less viscous? We performed
numerical experiments where for a fixed surface tension C, force G, viscosity
ratio B and experiment length
t
final
, a cleft formed; the same rudiment under iden-
tical conditions but whose mesenchyme/ECM was 10 times as viscous (B multi-
plied by 10)
failed
to form a visible cleft in the same time period (Figure 5).