Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
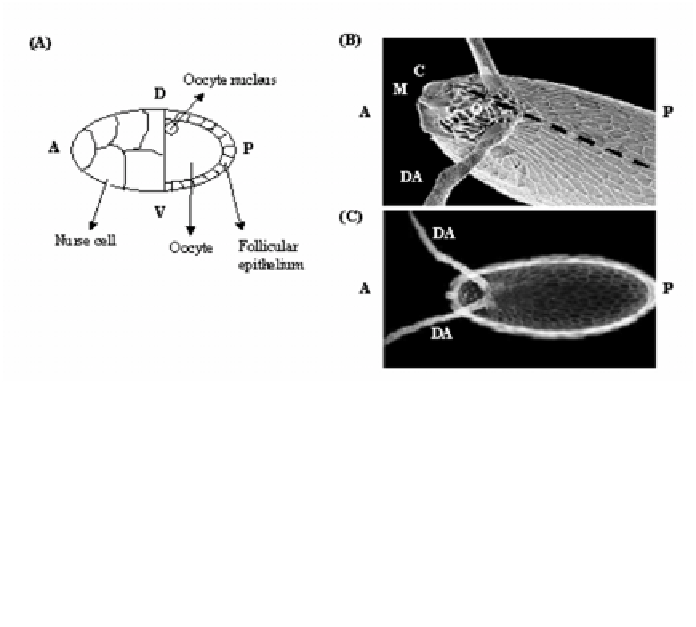
Figure 3
. (
A
) A mid-stage egg chamber. At this stage, the nucleus has just migrated from the
posterior to the future dorsal position (A = anterior, P = posterior, D = dorsal, V = ventral). (
B
)
A scanning electron micrograph of the dorsal-anterior section of a mature egg chamber (19).
(Reproduced from (19) with permission "Development," Company of Biologists.) Specialized
regions can be identified: the micropyle (M), the entry point of the sperm; the operculum (O), a
distinct region between the dorsal appendages (DA) that serves as the larval exit door; and the
collar region (C), which delineates the operculum. The broken line indicates the midline (i.e.,
the dorsal-most aspect of the egg). (
C
) A dark micrograph of a mature fly egg chamber with the
dorsal appendages extending out from the dorsal-anterior side.
2.2. EGFR Signaling in Oogenesis: Eggshell Patterning
A fly egg is composed of three types of cells (Figure 3A): the oocyte, which
later develops into the embryo; the nurse cells, which supply nutrients to the
oocyte; and the follicle cells, which form an epithelium enveloping the oocyte.
The EGFR-mediated patterning of the follicle cells is highly regulated in space
and time (17,18). The net result of this patterning process is division of the ini-
tially equivalent follicle cells into distinct populations. Each population of folli-
cle cells gives rise to a specialized structure of the eggshell. EGFR signaling
first divides the follicle cells into dorsal and ventral cells. Afterward, EGFR
signaling further subdivides the dorsal cells into several subpopulations that give
rise to different dorsal structures (Figure 3B) (18). Here we focus on the respira-
tory appendages extending from the dorsal-anterior side of the egg, whose posi-
tioning along the dorsoventral axis requires EGFR signaling (Figure 3C) (20).
Gurken is localized around the oocyte nucleus throughout egg development
(21). The relevant patterning process starts during mid-oogenesis, at the time
when the oocyte nucleus has just migrated from its previous posterior position
to a random point along the oocyte anterior circumference (22,23). Gurken