Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
t
2
t
2
p
3
t
4
t
4
p
6
t
6
K
p
1
t
1
t
1
p
2
p
5
t
3
t
3
p
4
t
5
t
5
p
7
t
7
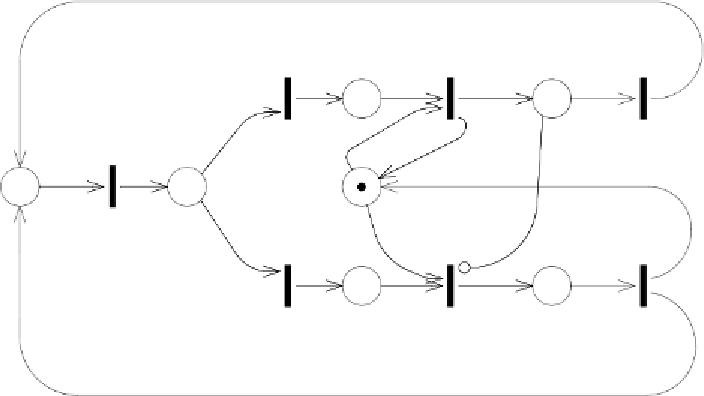
Figure 2.1: A Petri net model
obtain a class of models that have a fully specified initial marking. Predicates
allow the specification of restrictions over the set of admissible parameter
values, and/or the relations among the model parameters.
As an example, in Fig.
2.1
the graphical representation of a PN model is
shown. It comprises seven places (P =
{
p
1
,p
2
,p
3
,p
4
,p
5
,p
6
,p
7
}
) and seven
transitions (T =
{
t
1
,t
2
,t
3
,t
4
,t
5
,t
6
,t
7
}
). Transition t
1
is connected to p
1
through an input arc, and to p
2
through an output arc. Place p
5
is both
input and output for transition t
4
. Only one inhibitor arc exists in the net,
connecting p
6
to t
5
. Only two places are initially marked: p
1
and p
5
. The
former contains a parametric number of tokens, defined by the parameter
K (restricted by the predicate K
≥
1), while the latter contains one token.
According to the definition of parametric initial marking, this initial situa-
tion can be expressed with the vector [K, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]; a more convenient
notation (that will be often used throughout the topic) for expressing this
same situation is however Kp
1
+ p
5
(a formal sum denoting the multiset on
P defined by the marking).
The PN model in Fig.
2.1
is a description of the well-known readers &
writers system, where a set of processes may access a common database
either for reading or writing. Any number of readers may access the database
concurrently; instead, a writer requires exclusive access to the resource. This
example will be used throughout the chapter for illustrative purposes, since it
comprises three interesting aspects of parallel systems: concurrency of events
(two processes may be concurrently accessing the database for reading),


Search WWH ::

Custom Search