Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
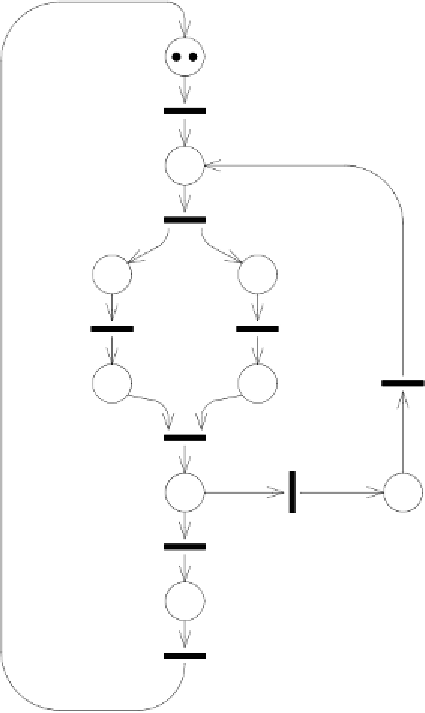
t
newdata
t
start
t
par1
t
par2
t
check
t
syn
t
KO
t
OK
t
I/O
Figure 1.8:
PN description of a parallel system
fork operation — firing of t
start
). When both processes complete (firing
of t
par1
, and t
par2
, respectively), a synchronization takes place (the join
operation — firing of transition t
syn
). The consistency of the two results is
then controlled, and one of the two transitions t
OK
or t
KO
fires, indicating
whether the results are acceptable, or not. If the results are not consistent,
the whole computation is repeated on the same data, after a further control
(firing of t
check
); otherwise, the results are output (firing of transition t
I/O
),
and a new set of data is considered.
It must be observed that the PN in Fig.
1.8
contains a new construct,
formed by the two transitions t
OK
and t
KO
. These two transitions, together
with their input place, model a choice, and form what in PN terms is called
a free-choice conflict. The name conflict indicates the presence of a choice

Search WWH ::

Custom Search