Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Application of solid catalysts for the vapor-phase oxidation of simple,
small-chain alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds is well estab-
lished [117-119]. h e reasonable volatility and thermal stability of reactant
and product make it suitable for gas-phase reaction. But in the case of com-
plex molecule synthesis, gas-phase reaction is not suitable because the mol-
ecules do not have reasonable volatility and thermal stability. Solid catalysts
active in the liquid phase under mild conditions have a much broader appli-
cation range [120, 121]. A major challenge in liquid-phase oxidation with
solid catalysts is to prevent leaching of the active species [122]. Supported
noble metal catalysts are active for oxidation of dif erent types of alcohol
and polyols. Platinum and palladium metals are most commonly used for
alcohol oxidation reaction under mild conditions using molecular O
2
as an
oxidant. Dif erent types of promoters such as Bi, Pb, Cd, Co, Cu, Se, etc.,
are used for alcohol oxidation reaction. Today, various bi- and multimetal-
lic catalysts are applied that are more active, more selective, and less prone
to deactivation than monometallic catalysts. h e probable redox model for
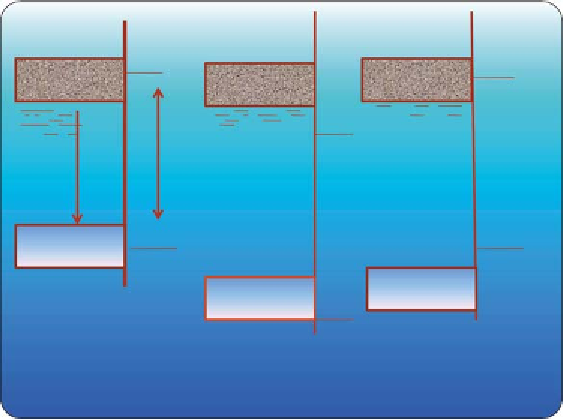
selective oxidation reaction is shown in Figure 8.29.
Oxide and mixed oxide catalysts are potential catalyst for alcohol oxi-
dation, dehydrogenation reaction, etc. h ese catalysts are mainly used for
the gas-phase oxidation reaction by using molecular oxygen, dehydroge-
nation reaction, etc. Hydrated ruthenium oxide and vanadium pentoxide
Hydrocarbon
E
redox
E
redox
e
Hydrocarbon
E
F
Hydrocarbon
E
F
E
redox
Oxygen
e
E
redox
E
redox
Oxygen
Oxygen
E
redox
Catalyst is not
reoxidized
Catalytic oxidation of
hydrocarbon molecule
can proceed
Oxidation of hydrocarbon
cannot proceed, Molecule is
not activated
Figure 8.29
Probable redox model for the
selective oxidation reaction.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search