Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Comp strength (kg/cm2)
Water absorption(%)
Shrinkage (%)
Density (g/cc)
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
CCRs(%)
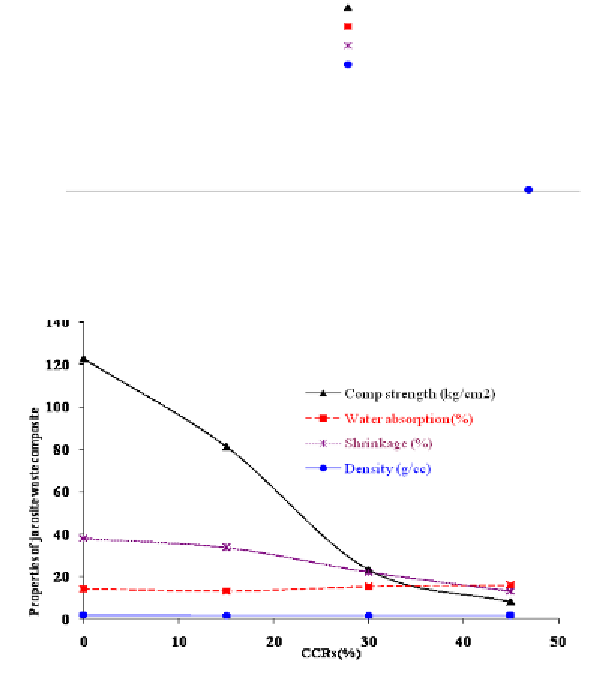
Figure 9 (c). Effect of CCRs on the mechanical properties of jarosite composites made
using jarosite waste to clay ratio 3 with CCRs.
Figure 9 (d). Effect of CCRs on the mechanical properties of jarosite composites made
using jarosite waste to clay ratio 4 with CCRs.
3.2.3. Effect of Sintering on Mineralogy and Microstructure of s/s
Jarosite Products
Firing of clay products leads to mineralogical, textural, and physical
changes that influence their quality. During high temperature firing, the
reaction behavior of temper grains (jarosite waste- clay matrix) is dominated
by dis-equilibrium conditions and characterized by the presence of different
reacting substances. When firing clay or compounds of silica and alumina
above 900 ºC, new crystallite phases are formed which are Al-Si spinel and
mullite (Peters and Iberg, 1978); Lingling et al., 2005). This is further
confirmed by earlier work on clay and pottery firing (Qrts, et al., 1993;



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search