Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
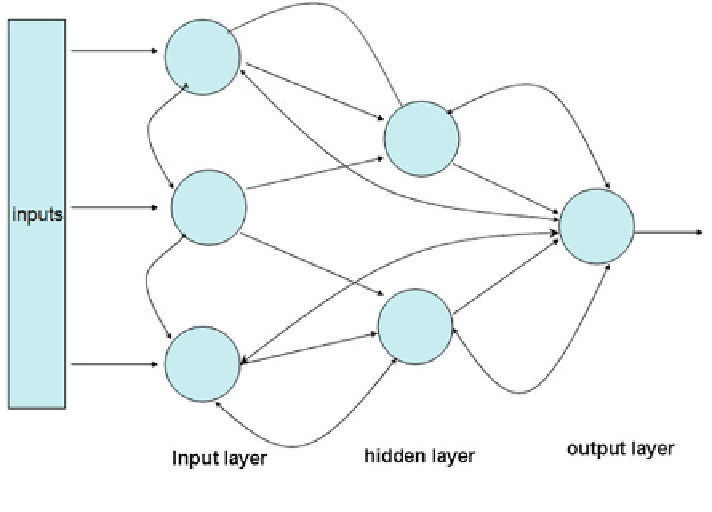
Fig. 4.5 Topology of a recurrent neural network
hydrological applications we normally use the Elman ANN with sigmoid arti
cial
neurons in its hidden layer, and linear arti
cial neurons in its output layer. The
topology of the Elman network is shown in Fig.
4.6
.
4.3.4 Jordan Artificial Neural Networks
The schematic view of a Jordan net is shown in Fig.
4.7
, from which one can
identify the major differences between the Jordan and Elman recurrent neural
networks. In a Jordan network, the context layer is connected to the output layer
instead of hidden layer. The context layer holds the output values from the previous
step and then echoes back to the hidden layer. This model was developed by
Michael I. Jordan in 1986 [
43
].
4.3.5 Hop
eld Networks
This type of recurrent neural network was introduced by John Hop
eld [
35
].
Hop
eld networks include a group of interconnected neurons which asynchro-
nously update its activation function. Because of its parallel architecture, these
models are well suited for real life systems (debatable!) and gave better dynamism