Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
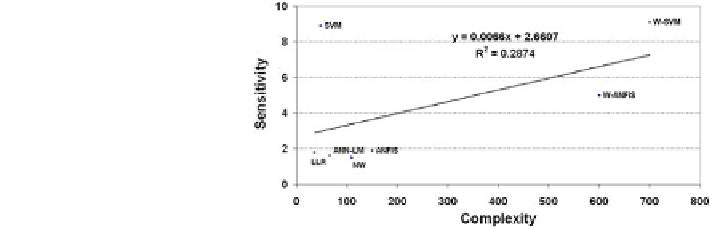
Fig. 5.46 Sensitivity versus
complexity
—
case study: solar
radiation modelling
overall model utility index Overall Model Utility index (U) varies between 0 and 1.
If the value of U is larger which means that model is useful to make reliable
predictions in solar radiation modelling. The pictorial output of the variation of
utility index value for different models is shown in Fig.
5.47
.
It has observed that the utility value is high for relatively complex NW model
and followed by ANFIS, W-ANFIS, LLR, W-SVM and SVM model. It is inter-
esting to note that the ANFIS model has better utility than the hybrid form
W-ANFIS. It has been found that in the case of ANFIS, the wavelet incorporation
didn
t provide the expected gain. The conjunction of DWT and ANN is found very
useful as observed in the higher overall model utility (U) value. The complex model
W-SVM couldn
'
t produce a higher prediction results with minimal variability.
Because of the higher sensitivity to changing inputs, the SVM and W-SVM models
exhibited relatively low utility value. Relatively less complex LLR model produced
reasonable results and the utility value of LLR models were higher than that of the
SVM, W-SVM and LM algorithm based ANN model (ANN-LM).
'
Table 5.3 Different models and their attributes which decides overall model utility in solar
radiation modelling
Models
Complexity
(function of
training
time)
Sensitivity
(slop of the
sensitivity
curve)
RMSE
(W/m
2
)
RMSE
(relative
fraction of
higher
value)
Sensitivity
(relative
fraction of
higher
value)
Utility
(U)
NW
109
1.5236
9.88
0.32813
0.167245
0.739577
SVM
48
8.911
17.165
0.570076
0.978156
0.199445
ANN-
LM
66
1.6295
30.11
1
0.178869
0.281671
ANFIS
150
1.904
14.835
0.492693
0.209001
0.621564
W-
ANFIS
603
4.9825
15.345
0.509631
0.546926
0.471392
W-
SVM
706
9.11
15.31
0.508469
1
0.206734
LLR
35
1.8049
24.83
0.824643
0.198123
0.400296