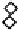Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
9
6
10mM
3
1mM
0
0
3000 6000 9000 1200015000
Leaching volume(mL)
9
6
10mM
1mM
3
0
0
2000
4000
6000
Leaching volume(mL)
Figure 2. The effects of different concentration of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the soil P
release with leaching (left: citric acid; right: malic acid).
Table 3. The effects of different concentration of organic acids on the soil P release
with soft leaching
V(min)
(ml)
P(maxi)
(mg/kg)
P/T(maxi)
(%)
P(cumulative)
(mg/kg)
P/T(cumulative)
(%)
Concentration
Citric
acid(10mM)
310
8.4
1.1
469.1
62.7
Citric acid(1mM)
1990
0.93
0.1
129.7
17.3
Malic acid
(10mM)
430
5.4
0.7
507.8
67.9
Malic acid
(1mM)
2640
0.42
0.06
17.3
2.3
(V(min): least organic acid for P release; P(maxi) and P/T(maxi): maximum phosphorus and rate of
total phosphorus released at leaching experiment; P(total) P/T(total): cumulative phosphorus and
cumulative rate of total phosphorus released at leaching experiment).
The total amounts of phosphorus leached by citric acid and malic acid in a concentration
of 10mmol L
-1
were respectively 3.5 and 32.6 times of the amounts leached when citric acid
and malic acid were in a concentration of 1mmol L
-1
. Meanwhile, the start point and peak of
phosphorus leaching were also affected by the concentrations of citric acid and malic acid.
For citric acid and malic acid, when their concentration declined from 10 to 1mmol L
-1
, the
start point of phosphorus leaching was also delayed correspondingly, indicating that the lower