Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
d
c
Figure 3.1
. Four types of covariance structures that may be used in the matrix normal
perturbtion model: a) independent and same variances (isotropic); b) independent and
different variances; c) correlated landmarks and uncorrelated axes; d) correlated land-
marks and correlated axes. We generated 100 matrix Normal random variables under
different covariance structures and plotted these in the original coordinate system
without introducing any rotation, translation or reflection. Visually, it is difficult to dif-
ferentiate the first three covariance structures. However, the statistical inferences
estimated from these different covariance structures (e.g., confidence intervals) are
quire different under these different covariance structures. The mathematical details
of the various covariance structures conveyed graphically in f 3.1, are provided in
Part 2 of this chapter.
We will consider four different types of covariance structures
(graphically presented in
Figure 3.1
)
, chosen for both statistical and
biological reasons. Statistically, these four types of covariance struc-
tures are amenable to analysis using a sample of arbitrarily rotated
and translated objects. Biologically, these covariance structures seem
reasonable and appropriate, reflecting expectations gained through
experience with data collected from biological populations.
Mathematical details of the various covariance structures conveyed
graphically in
Figure 3.1
,
are provided in
Part 2
of this Chapter.

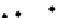
















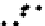


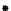

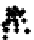





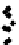



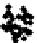

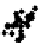




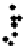





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search