Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
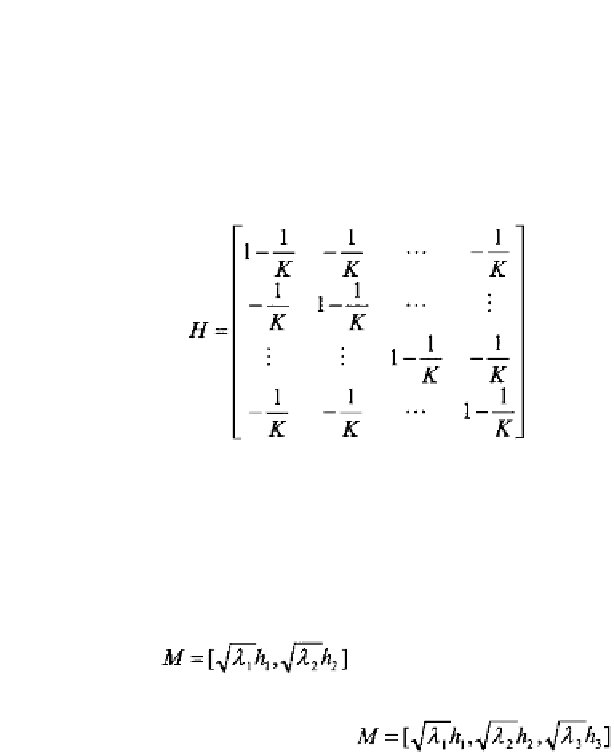
where
is a
K
K
symmetric matrix.
The eigenvalues (
1
>
2
>
3
> ...
K
) and eigenvectors of
B
(
M
) are cal-
culated next. The eigenvalues are arranged in decreasing order by
1
,
2
,
K
, and the corresponding eigenvectors are given as
h
1
,
h
2
, ...,
h
n
. Note that
h
1
,
h
2
, and
h
3
are
K
x 1 vectors, and
1,
2, and
3 are
positive real numbers provided the hypothetical form is a three-dimen-
sional object. If the original data are from two-dimensional objects, the
estimate of the coordinates of the hypothetical form matrix is given
3
, ...,
by . If the original data are from three-
dimensional objects the estimate of the coordinates of the hypothetical
form matrix is given by
.
The landmark coordinate locations for the hypothetical form from
our example are given below.
Coordinates of the Hypothetical Form
0.93655
-0.89435
0.88308
2.16769
1.01905
0.03706
1.66302
0.10050
-0.66443
-0.77885
-1.54961
-0.51053
-2.33166
0.81673
-0.32909
-1.65674
0.50768
0.58390
These coordinate data for the hypothetical form can be translated and
rotated so that the form appears in a biologically sensible orientation
when viewed. Coordinate locations obtained in this way can be used to
graphically represent the hypothetical form, but we stress that the
estimator is a representation of the hypothetical form only up to rota-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search