Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
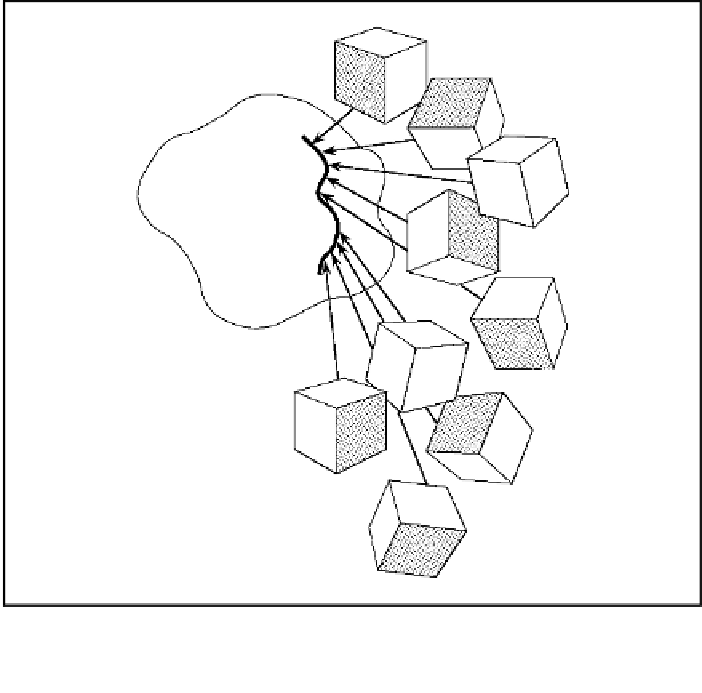
Figure 4.6.
Graphic representation of an orbit for a cube of specific dimensions with
eight landmarks. All rotated, reflected, and translated versions of the 8x3 matrix rep-
resenting this cube map to the orbit depicted as a curve.
form under study belongs in the space of all
K
D
matrices. We can-
not know the exact location of the original
K
D
matrix on the
identified orbit.
Now, suppose we know that the hiker started his hike at elevation
of 2000ft. above sea level but he is now at an elevation of 2560ft. We
know the contour on which the hiker started and the contour that he
presently occupies, but we have no information regarding his exact
starting place, nor his exact location at the current elevation. This is
analogous to the problem of form comparison. We know the orbit of the
first form and the orbit of the second form, but we do not know the
exact location of the forms on their respective orbits.
If our information is limited to elevation, we can only know that the
hiker has ascended 560 vertical feet. This finding is invariant to the
exact location of the hiker on the initial contour and invariant to the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search