Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Storage Provisioning
To use disk volumes for storing data, you must create a LUN, which can be mapped to any
host, cluster, or data center (Figure 9.4). Once mapped, a volume can be mounted on a VM
and used for storing data.
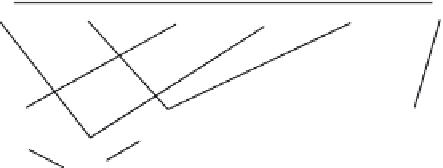
FIGURE 9.4
LUN network mapping
Data center
LUN
LUN
LUN
LUN
LUN
LUN
LUN
Logging server
SQL Server
Though a disk volume may be mounted to only one host at a time, it can be shared
between a number of hosts or VMs. This is termed as
network sharing
or
sharing a resource
.
A disk volume can be remotely but transparently accessed from another computer using net-
work sharing techniques.
In a SAN, devices requesting I/O operations are initiators and devices performing these
operations are targets. FC zoning, as explained earlier, is implemented at the hardware
level and configured on a per-target and initiator basis. In a SAN, access must be granted
to appropriate storage devices (or logical units, as they are referred to in this context). LUN
zoning provides a method of configuring initiator-target relationship.
LUN masking can enable you to further constrain the access to ensure that only devices
authorized to access a specific initiator (a server host) may access the corresponding port.
This method subdivides access to a given port. In such a case, several LUNs can be accessed
through the same port, but server masks limit each server's access to only allowed LUNs.
LUN masking is typically conducted at the switch or HBA level.
A usual big future challenge is to add more capacity to SANs. One way is to add more
physical devices. This of course means that the system has to have empty and open slots
and the cabling necessary for installation. The key challenge here is the change in configu-
ration and incurred downtime, or at least some interruption of service.
Another option is to add an additional node. In this case too, installation and con-
figuration require planning. The biggest advantage of this approach is to provide higher
availability, failover, and an opportunity to scale up not only capacity but also perfor-
mance. The key challenge here is to balance performance and capacity. Adding only
capacity may create performance bottlenecks.


















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search