Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
As discussed in chapter 8, the use of the right
type of container for growing each plant
species combined with periodic inspections
of the plants at the nursery where they are
being grown should prevent most of these
problems from occurring.
Various planting techniques are available
depending on the type and size of plant prop-
agules selected. For example, woody cuttings
can be inserted by hand, pounded into the
ground with a mallet, placed in shallow
trenches and covered with soil (willow wat-
tles), installed with a waterjet stinger, shoved
through riprap with a stinger, or installed
with a hand soil auger, a handheld power au-
ger, or a power auger mounted on a vehicle.
There are proper ways to dig holes for
plants and to install container stock. Under
certain soil conditions, roots cannot spread
into the surrounding areas unless the sides of
planting holes are scarified. Plant roots en-
circling their container need to be pruned.
Some plants are unlikely to survive if they
are installed too deep or too shallow. There
should be no air pockets around the roots,
and aerial stems must be erect or nearly so.
Volunteers need supervision on these points.
Large blocks of vegetation (sod slabs) can
be translocated using a skip loader, a larg-
er sod cutter, or a similar modified tool for
scooping up wetland and herbaceous vegetation along with the soil and root systems. Sod slabs
have been stacked on top of one another like steps to construct or stabilize stream banks in mead-
ows. If there is a lag time between when the sod slabs are harvested and when installation can
occur, the slabs need to be kept in a holding area and watered as needed.
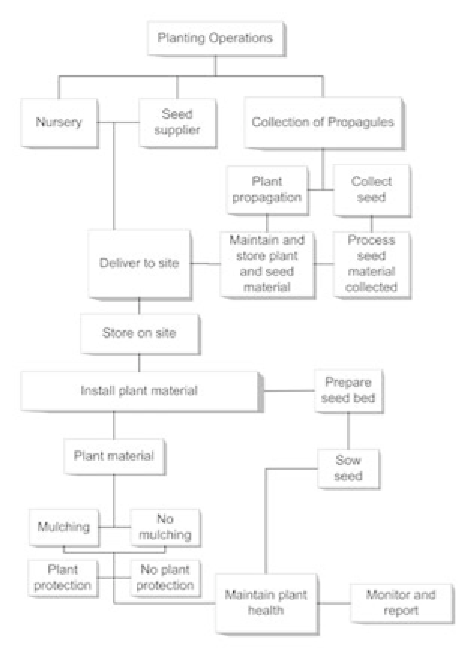
FIGURE 10-6.
Planting operations can be involved,
so understand the material and tasks needed as
well as the time needed from ordering to delivery
on-site. Incorporate these time frames into your
schedule.
Installation of Plant Protection
Decisions concerning plant protection devices will be resolved during the design phase. Table 10-1
lists several of these devices. The efficacy of many types of plant protection devices that can be
purchased or fabricated has been tested with respect to plant survival, growth, and the prevention
of browsing impacts (Hall, Pollock, and Hob 2011).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search