Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Water
Site suitability and the time of year during which the plant materials are installed will determine
the need for a supplemental water supply. If you are modifying existing topography adjacent to
a water source, and you have determined the water regime so that the site will be exposed to
sufficient water shortly after planting or seeding, then supplemental water may not be necessary.
However, if the site is elevated and intended for only occasional flooding, as in the case of benches
or terraces adjacent to streams and rivers, then providing water to allow for root growth will need
to be addressed. If you have control over the planting or seeding time, and the rainfall or flooding
is fairly predictable, you may have an acceptable risk level for not providing supplemental water.
Obviously, wetland systems operate under a different hydrological regime than uplands. You may
need to calculate the water budget for your project to ensure that sufficient water will be available
to promote plant growth (Pierce 1993).
Understanding how the hydrological factors are at work on your project site is necessary to
ensure successful plant establishment. Water can occur on your site naturally through natural
watercourses, ponds, or seeps. Water in the subsurface, commonly called groundwater, tends to
fluctuate with the season. Water from rainfall changes watercourses or changes the level of water
bodies, such as ponds or lakes. Knowing how water behaves on your site will influence several
decisions you must make. How will you go about restoring your site? When will you attempt the
restoration effort? What material or equipment or agreements will you require?
For projects designed to use only naturally occurring water, the timing should coincide with the
time of year when water is available and plant growth will occur. Dormant plants allow for a plant-
ing program without the need to have water available until the breaking of dormancy. The instal-
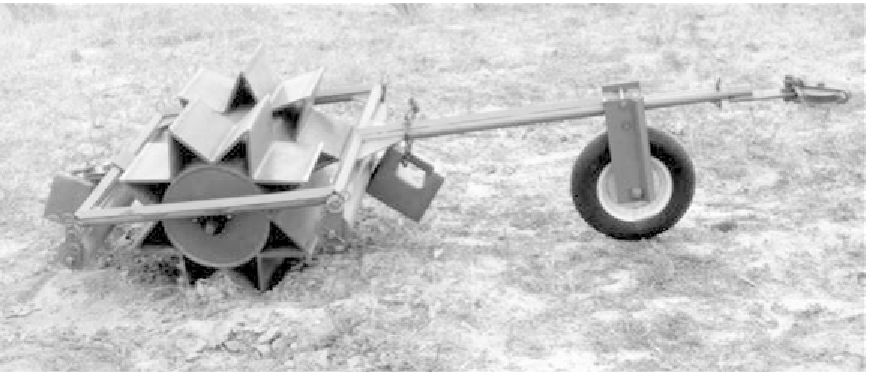
FIGURE 7-1.
Imprinter device used for creating catchments for seed and water to promote plant estab-
lishment on coastal slopes. Different designs of the imprinter are used extensively in arid land situations.
(Photo by Mary F. Platter-Rieger.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search