Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Physically
adsorbed moisture
Step 1
NP
5.1 g
NP
NP
+
C:1.03 g
NP
P:1.42 g
Physicochemical
adsorption of catalyst
and promoter
Ultrasonic bath: 30 min
Step 2
P
NP
7.7 g monomers
Ultrasonic bath: 6h
Step 3
THF
NP
NP/PU
composite
SIP NP/PU
Aluminum mold:
3 days
Hot press: 130°C
10 min
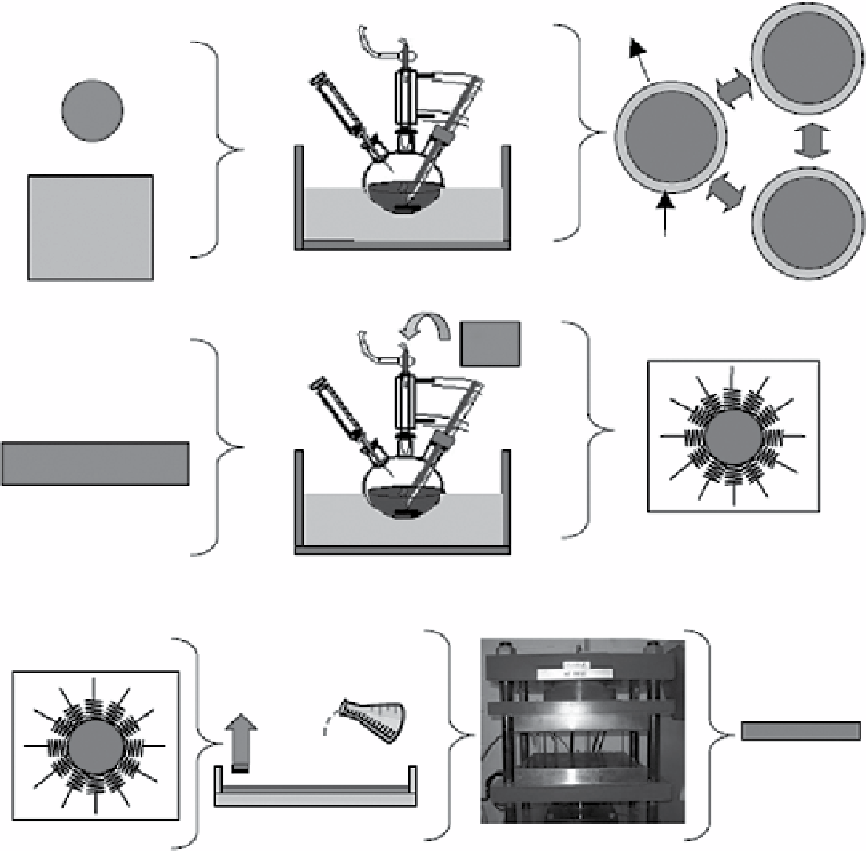
figure 4.1
Schematic of the surface-initiated polymerization (SIP) process. Adapted with permission from Ref. [16]. © IOP.
magnetic and dielectric properties. The PNC samples synthesized using the SIP method showed negative permittivity in contrast
to the positive real permittivity in the PNCs prepared by physical mixing. Moreover, positive MR was observed in all the PNCs,
which was analyzed by the wave function shrinkage model. The external magnetic field contracted the electronic wave function
at the impurity center, while the introduction of barium titanate reduced the contraction effect and thus PNCs showed lower
magnetic resistance than the neat PANI.
The MSP method usually avoids the use of additional surfactants, but instead the monomer itself serves as the coupling
agent with one end bonding to the NP surface and the other continuing polymerization with other monomers, thus forming a
well-dispersed and uniform PNC network. For example, through this unique MSP method, a robust entity of Fe/vinyl ester
resin nanocomposites was fabricated, which demonstrated enhanced mechanical strength [17]. Figure 4.2 shows a scheme in
which iron NPs are stabilized by vinyl ester monomer and facilitate further polymerization with other monomers, thus forming
the interconnecting system. In addition, we have also successfully prepared PP- and Pe-based PNCs by in situ thermal decom-
position of the organometallic iron precursor in the polymer solution at high temperatures [19-22] in which size- and phase-
controlled iron NPs were synthesized in situ and uniformly dispersed in the polymer matrix to form PP or Pe magnetic
nanocomposites.