Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
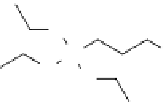
The amines ethylene diamine (EDA), tetraethylenepentamine (TEpA),
N
-dimethylaminopropyltrimethoxysilane (DmApS),
3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (ApTS), and polyethyleneimine (pEI) are the most common compounds used in CNT modification
reported in the literature.
H
N
H
N
H
2
N
H
2
N
NH
2
N
H
NH
2
EDA
TEPA
O
O
O
NH
2
Si
Si
O
N
O
O
DAMPS
APTS
NH
2
H
2
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
H
NH
NH
2
n
H
2
N
PEI
21.3.1.2.1 Amine-Modified Carbon Nanotubes
The chemical modification of the CNTs with functional groups containing
amine groups improved the capacity to capture CO
2
. CNT interactions with gases may be tuned for chemisorption interactions
through the functionalization of the nanotube surface with various functional groups. Covalent functionalization of SWCNTs
has also been well studied [45] and can be performed by facile acid treatment, which creates hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxylic
acid (-COOH) groups on the ends and walls of the SWCNTs [46]. The enhancement occurs because of the acidity of CO
2
, a
Lewis acid molecule, which prefers to adsorb on a nitrogen-rich basic surface.
Some conditions affect the efficiency of adsorption of CNTs. In general, in comparison to typical commercial adsorbents,
such as zeolites [47], the performance of CO
2
adsorption on amine-modified CNTs increases with the presence of moisture till
a certain limit, and then decreases. In most cases, the adsorption decreases with the increase in temperature due to changes in
the mechanisms of interaction and the initial CO
2
concentration also displays an interesting behavior.
The general proceedings for testing CNT adsorption capacity in the laboratory recommend a stream of CO
2
with a
concentration between 2 and 50%, which was selected as representative of various CO
2
emission levels from combustion in
industrial activities, fossil fuel power plants, coal gasification systems, and confined spaces like submarines and space capsules.
A range of temperatures between 20 and 100°C, preferably 50°C, is used to simulate a typical flue gas from an industrial oper-
ation. The selection of water vapor typically ranges between 8 and 12% in a flue gas [48].
21.3.1.2.2 Effect of Temperature
Su et al. observed the adsorption isotherms of CO
2
via mWCNTs impregnated with
ApTS at temperatures ranging from 20 to 100°C. Comparing the differences in the capacity of CNTs with and without
amine modifications (Fig. 21.12a), the results showed an increase of 1.5-2.0 times in the
q
e
for the latter. Another interesting
work from Ye et al. [49] reports the adsorption of low concentrations of CO
2
with carbon nanotubes (mWCNTs) impregnated
with TEpA, a long aliphatic amine with primary and secondary amine groups, at temperatures ranging from 282 to 313°C.
They evaluated the adsorption capacity of CNT sorbents with four different TEpA loadings: 10 (CT-10), 20, 30, and 40%.
Figure 21.12 shows the adsorption capacity curves. Contrary to the expected results, the adsorption capacity of the raw
CNTs experienced a modest increase to 0.49 mmol g
−1
from 283 to 298°C and then a gradual decrease to 0.33 mmol g
-1
with