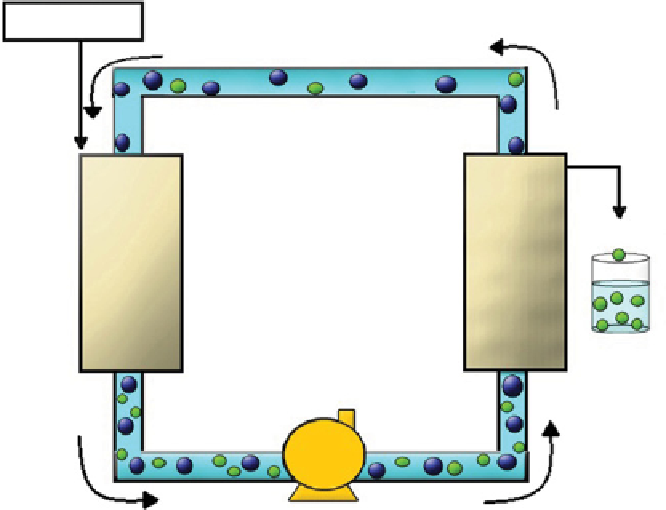
Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Solvent in
Retentate
reservoir
Dialtration
membrane
Permeate
Peristaltic
pump
FiGurE 19.4
Schematic representation of the experimental setup maintained by Sweeney and coworkers. In this experiment, the sample
containing soluble nanoparticles (NPs) was added to the reservoir; this was pumped through the filter membrane. The filter membrane filters
the smaller particles while retaining the larger particles. The filtration process that takes place in the diafiltration membrane is also shown in
an expanded manner. This figure has been modified from Sweeney et al. [69].
7.
Extraction
: The process of extraction mainly involves the separation of compounds on the basis of their relative solubil-
ities in two different immiscible liquid phases, the most common being water and an organic solvent. Both organic and
inorganic compounds have been separated by this method. For example, gold and silver dendrimer-encapsulated NPs
have been separated by this method [70].
8.
Other purification techniques
: Many other techniques have also been used for the purification of NPs. One, not so
popular, technique is the use of supercritical ethane for the purification of NPs, which has been used to purify alkanethiol-
stabilized gold NPs [71]. Another technique used to purify NPs based on the shape involves the use of surfactants like
cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) because these surfactants have the ability to precipitate rods and platelets in
a concentrated solution while not affecting spherical NPs [72]. Other techniques include micelle induction [73, 74], the
use of ultrasound-assisted phase transfer for shape-dependent separation [75], and periodic precipitation [76].
19.11
ApplicAtionS oF nps
The application of NPs has been extended to multiple fields. Especially in the fields of medicine and the environment it holds
distinct advantages and is being applied extensively. From the early days, silver salts have been used in many novel therapies
such as for the treatment of nicotine addiction and mental illness. It has also been used in the treatment of diseases like syphilis
and gonorrhea [77-80]. The main advantage of NPs is their higher surface area due to which they have higher reactivity [81],
and these unique properties are not exhibited by them in their bulk nature. The antibacterial property of nanosilver has been
widely used in various applications such as in bandages, wound dressing, and ointments [82]. According to some theories, silver
ions released from NPs have the ability to inactivate essential bacterial enzymes, drain intracellular Adenosine triphosphate
(ATP) levels, hinder dNA replication in bacteria, damage the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria, and in the end cause cell lysis
[83]. A coat of Pd on nanosilver enables them to be used as a catalyst, and it can also be used to treat pollutants in groundwater
efficiently [84]. Immobilization of certain enzymes on NPs is found to have a direct impact on their stability. Upon immobili-
zation, controlled release of the enzyme is possible thereby improving the reactivity of the enzyme, and it also has an additional
advantage in that it shields the enzyme from degradation [85]. This antibacterial property of silver can be augmented when it is
persists for a longer time in a specified location, and by controlled release of silver NP this is possible. dlugosz M and his