Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
2.20
1.80
1.40
1.00
0.60
0.0
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
10.0
Cluster diameter (nm)
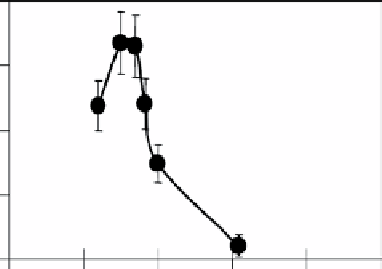
figure 10.2
(a) Size dependence of the morphology of gold clusters on the TiO
2
(110) surface; (b) relationship of the cluster diameter to
photocatalytic activity. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [55]. © 2002, Academic Press.
5nm
figure 10.3
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy image of a gold cluster on a TiO
2
surface. Reproduced with permission
from Ref. [56]. © 2004, Springer.
band gap and thereby expand the spectral range of absorbed wavelengths. Doping may be carried out either by ion implantation
or by chemical processes such as sol-gel. extensive research activity followed initial success in using ion implantation to inject
small amounts of cr and V that resulted in increased photocatalytic activity [60, 61]. cations occupy substitutional Ti lattice
sites and cause a red shift of the absorption band by an amount dependent on the implantation energy, which determines the
depth distribution of the implanted ions. Doping with other metals, such as fe, Ni, Rh, mn, and Nb, produces similar effects to
varying degrees. Interestingly, no effect is observed for implantation with Ar, mg, or Ti, suggesting that the absorption shift