Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
120
100
MWCNT-reinforced Fe-PAA/PVA
MWCNT-reinforced PA A/PVA
80
60
40
20
0
0
30
60
90
C
e
(ppm)
120
150
180
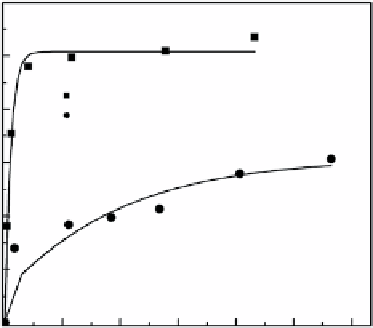
figure 6.8
The Cu(II) ions sorption isotherms (contact time: 60 min; [mat] = 0.5 mg/ml). reprinted with permission from ref. [19],
pp. 48-54. © 2011, Elsevier.
6.5.2
Heavy Metal ion remediation
For toxic heavy metal ion remediation, electrospun PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats have been used to remove copper (II) ions from
aqueous solution [15]. The PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats were able to remove about 98% of Cu(II) in the initial 30 min at room
temperature. The Cu(II) removal is attributed to the strong complexation effect of free carboxyl group of PAA with Cu(II) ions
[76, 77]. In addition, the water-stable PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats displayed excellent selectivity in the absorption of Cu(II) in
the presence of both Cu(II) and Ca(II) ions with the same concentration. Furthermore, it was shown that under the selected ionic
strengths ([NaCl] = 0, 0.1, and 0.5 M), the absorption capability of the cross-linked PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats was not signif-
icantly impacted. When compared with other materials used for heavy metal ion removal, the high surface area to volume ratio
of the porous PAA/PVA fiber material allows for complete interaction with the ions to be removed, thereby significantly
enhancing the capability of this material for environmental remediation.
by incorporating ZVI NPs within PAA/PVA nanofibers, heavy metal ions could be remediated via both physical absorption
and chemical absorption processes. In our recent study [19], MWCNT-reinforced PAA/PVA nanofibers immobilized with ZVI
NPs were also used to remediate Cu(II) in aqueous solution. Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution were removed using hybrid ZVI
NP-immobilized nanofibers under an array of varying conditions, including solution pH and contact time. We showed that Cu(II)
removal by hybrid mats containing ZVI NPs was not affected by pH variation and the removal percentage remained at around
91%. In contrast, the sorption ability of PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats without ZVI NP immobilization was affected by the pH
change: The Cu(II) removal percentage increased markedly with pH, presumably due to the fact that more carboxylic groups in
the PAA/PVA nanofibers became deprotonated, leading to favorable ion sorption via electrostatic interaction [76, 78]. Furthermore,
MWCNT-reinforced nanofibrous mats containing ZVI NPs were able to significantly remove Cu(II) within the first 30 min, and
then reached an equilibrium (75.3 mg/g) within 60 min. by comparison, the MWCNT-reinforced nanofibrous mats without ZVI
NPs exhibited a much lower level of Cu(II) sorption. Although the incorporation of MWCNTs within the nanofibers did not
enhance the Cu(II) removal ability of PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats, our results clearly suggest that the immobilized ZVI NPs
improved Cu(II) removal via a chemical reduction reaction. Figure 6.8 shows the results of isotherm experiments. In the case of
the ZVI NP-immobilized hybrid mats, sorption of Cu(II) increased sharply with the aqueous concentration below 12 mg/l at
equilibrium and then reached a plateau near 100 mg/g when the aqueous Cu(II) concentration was above 12 mg/l, indicating
saturation of the binding sites. For the mats that were not ZVI NP-immobilized, sorption of Cu(II) ions exhibited a gradual
increase and reached 61.4 mg/g when the aqueous concentration at equilibrium was 169.3 mg/l. obviously, the sorption capacity
of the hybrid mats was greatly enhanced in the presence of immobilized ZVI NPs.
6.5.3
dechlorination
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is a widely used chlorinated solvent, which is one of the common pollutants in soil and groundwater.
dechlorination of TCE is able to significantly reduce its toxicity. MWCNT-reinforced ZVI NP-immobilized electrospun
PAA/PVA nanofibrous mats fabricated by Xiao et al. have proven to be highly effective in the dechlorination of TCE [13]. The
results show that both ZVI NP-containing nanofibrous mats with and without MWCNTs exhibit excellent performance in the