Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
300
300
300
200
200
200
100
100
100
0
0
0
296 298 300
Potential Temperature (K)
0.01
0.012 0.014
Specific Humidity (Kg/Kg)
3
4
5
6
Wind Speed (m/s)
(a)
(b)
(c)
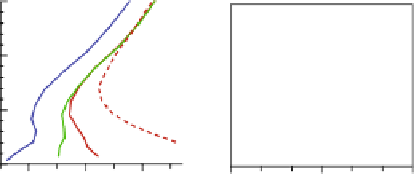
Fig. 6.11
Vertical profiles for the (
a
) potential temperature, (
b
) specific humidity, and (
c
)wind
speed off the coast (
line 1
), at the city centre (
line 2
) and over the peri-centre (
line 3
) (see locations
on Fig. 6.9) - same situation as Fig. 6.9. The profiles obtained at the city centre location in the
alternate simulation without city are also shown (
line 4
)
6.4 Conclusion
The experience gained from development, evaluation, implementation into ABL
numerical models, and the application of SM2U allows the following conclusions:
-
a “flat canopy” approach may be sufficient only when the city influence at large
temporal and spatial scales is evaluated;
-
building walls and small scale heterogeneities diurnal cycle of the fluxes and other
micro-climatological variables;
-
the role of walls materials in radiation and heat conduction during the day and
night need to be finely modelled to obtain the actual turbulent heat fluxes;
-
radiative trapping may be of less important due to self mitigation, although it may
be crucial for obtaining the canopy temperature. When the wind is very weak and
the air-wall temperature difference is very large, Sini et al. (1996) showed that the
aerodynamic transfer processes in the canopy layer may be significantly altered;
-
computing in parallel the energy and water budgets is very important in microcli-
matology simulations due to the strong interdependence at both small and large
temporal scales and the strong influence of the available humidity on the surface
and canopy temperatures. This is true even in the city centre where vegetation and
natural ground surfaces are limited because of the strong differences in air humid-
ity, and the specific behaviour of soil moisture, associated with heterogeneous soil
coverage.
References
Baklanov, A. and P. Mestayer (eds.), 2004: Improved parameterisations of urban atmospheric sub-
layer and urban physiographic data classification. / A. Baklanov, E. Batchvarova, I. Calmet,
A. Clappier, J.V. Chordá, J.J. Diéguez, S. Dupont, B. Fay, E. Fragkou, R. Hamdi, N. Kitwiroon,
S. Leroyer, N. Long, A. Mahura, P. Mestayer, N.W. Nielsen, J.L. Palau, G. Pérez-Landa,





Search WWH ::

Custom Search