Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
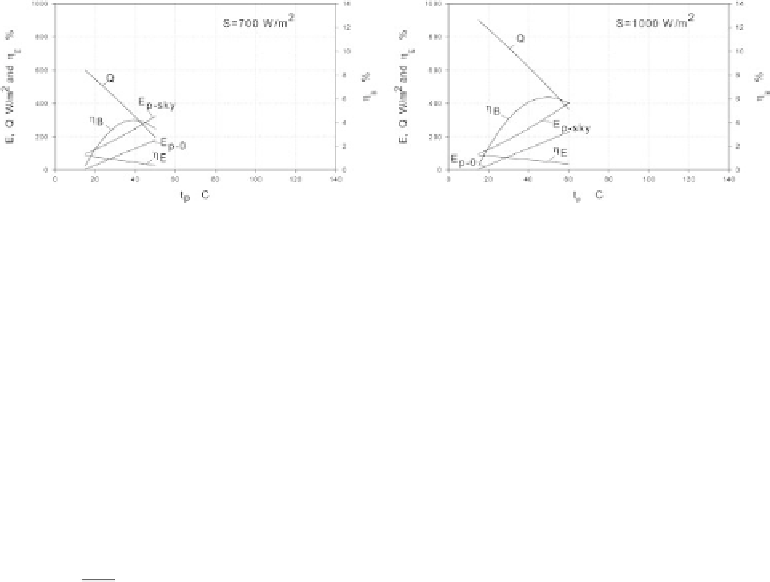
Figure 2.4.7
Plate exposed to solar radiation,
S
=
700W/m
2
(left) and
S
=
1000W/m
2
(right), (from
Petela, 2010).
E
p
−
0
=
Ak
p
−
0
(
T
p
−
T
0
)
(2.4.17)
and where
k
p
−
0
is the convective heat transfer coefficient. The harvest of the solar
energy can be determined by the energetic efficiency
η
E
:
Q
S
=
η
E
(2.4.18)
or by the exergetic efficiency
η
B
:
Q
ψ
c
S
(1
T
0
T
p
η
B
=
−
)
(2.4.19)
where
ψ
c
is the exergy/energy ratio discussed in paragraph 2.2.5. It can be shown that,
for the direct radiation of the Sun at its surface temperature 6000 K, the theoretical
value of the ratio is
ψ
=0.933. According to Gueymard (2004), the irradiance of the
direct solar radiation arriving at the Earth is 1366 W/m
2
. As the irradiance values
applied in the present canopy consideration are smaller then the exergy/energy ratio,
they could be taken as for a smaller irradiance temperature, e.g.,
ψ
c
=
0
.
9.
1m
2
,
k
p
−
0
5 W/(m
2
For example, assuming
A
=
=
K) and determined by the
287
.
16 K (14
◦
C), Fig-
ure 2.4.7 shows the calculation results for the two different values of irradiance,
S
=
·
T
1
.
5
0
=
Swinbank (1963) formula:
T
sky
0
.
0552
in which
T
0
1000 W/m
2
. With the increasing plate temperature
T
p
,(
t
p
C),
the energetic efficiency
η
E
decreases whereas the exergetic efficiency
η
B
is maximum.
In the second situation, shown in Figure 2.4.6b, the plate of the surface area 1 m
2
is a fragment of a very large and flat surface of the same uniformly distributed values of
temperature
T
p
and radiative properties. The plate is screened from the solar radiation
with a very large, flat and horizontal canopy. Material of the canopy can transmit
the whole solar radiation to the plate (canopy transmissivity
τ
SOL
=
=
700 W/m
2
and
S
=
1), although the
low temperature emission from the plate is entirely absorbed by the canopy (canopy
transmissivity
τ
PLA
=
0). The extreme values of these two transmissivities are assumed
to show better the effect of the canopy on the exchanged radiative heat. Due to a very
small thickness of the canopy the both its surfaces, that exposed to the Sun as well as
that exposed to the plate, have the same canopy temperature
T
c
.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search