Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
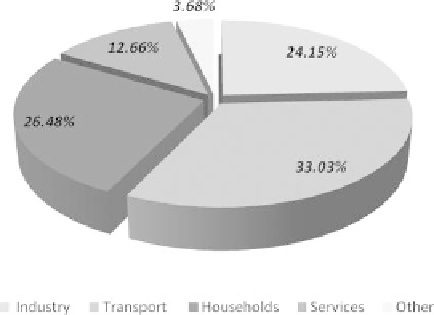
Graph 20.2.2
Final energy consumption in 2009, according to sector (Eurostat).
energy or eco-labels or other appropriate certificates or standards developed at
national or Community level, where these exist, as the basis for encouraging such
systems and equipment
9
.
In 2009, the final energy consumption of buildings in the EU continued to be
approximately 40% (see Graph 20.2.2). This total of 39.14% was mostly due to
energy use by households and services, whose consumption was largely dependent on
buildings (Eurostat, 2011a,b).
On 1 February 2012,
Directive 2002/91/C
was definitively repealed and replaced
by
Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of buildings
. This directive reaf-
firms the target of reducing energy consumption in the EU by 20% and justifies the new
regulations by highlighting the fact that buildings are responsible for 40% of the total
energy consumption
10
.
This obliges European countries to take measures to increase the number of build-
ings which not only fulfil current energy performance requirements, but which are also
more energy efficient. This will reduce energy consumption as well as carbon dioxide
emissions. EU member states are thus required to draw up national plans for increasing
the number of nearly zero-energy buildings
11
and to regularly report such plans to the
Commission.
9
Directive 2009/28/EC.
Article 13.6.
10
The Council of the European Union (2007). In the Council of March 2007, the European
Community decided to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20% compared to those in 1990.
The energy and environmental objectives to be achieved by 2020 are known as the 20-20-
20 targets. EU member states must thus do the following: (i) reduce by 20% the emissions
of greenhouse gases; (ii) increase by 20% the energy efficiency in the EU; (iii) reach 20% of
renewables in total energy consumption in the EU.
11
According to
Directive 2010/31/EU
, a nearly zero-energy building is a building that has a
very high energy performance, as defined in Annex I. The nearly zero or very low amount of
energy required should be covered to a very significant extent by energy from renewable sources,
including energy from renewable sources produced on-site or nearby.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search