Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
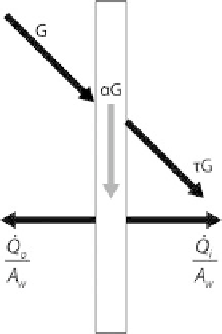
Figure 18.3.2
Irradiance G, absorption
α
G and secondary heat flows of single glazing outward and
inward.
difference between pane surface
T
s
and room air
T
i
or outside air
T
o
. Temperature
differences between the outside and inside surface are neglected.
Q
i
A
w
=
Q
o
A
w
=
h
i
(
T
s
−
T
i
)
h
o
(
T
s
−
T
o
)
(18.3.3)
From the heat flow balance, first determine the pane surface temperature
T
s
:
αG
=
(
h
i
+
h
o
)
T
s
−
h
i
T
i
−
h
o
T
o
(18.3.4)
αG
+
h
i
T
i
+
h
o
T
o
⇒
T
s
=
h
i
+
h
o
With this pane temperature
T
s
, the heat flow inward can be calculated:
Q
i
A
w
=
h
i
h
i
+
h
i
(
T
s
−
T
i
)
=
(
αG
−
h
o
(
T
i
−
T
o
))
h
o
h
i
h
i
+
1
(18.3.5)
=
h
o
αG
secondary heatflow
−
(
T
i
−
T
o
)
1
h
i
1
h
o
+
Transmission losses
Transmission heat losses of the glazing are calculated separately via the
U-value. Thus, for the definition of the secondary heat emission degree
q
i
,
the ambient
temperature can be set equal to the outside temperature The result for
q
i
is:
Q
i
/A
w
G
h
i
h
i
+
q
i
=
=
α
for T
i
=
T
o
(18.3.6)
h
o
For double-glazing, the characteristic values are calculated similarly, although an
additional heat balance for the outside pane must now be created. The absorption







Search WWH ::

Custom Search