Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
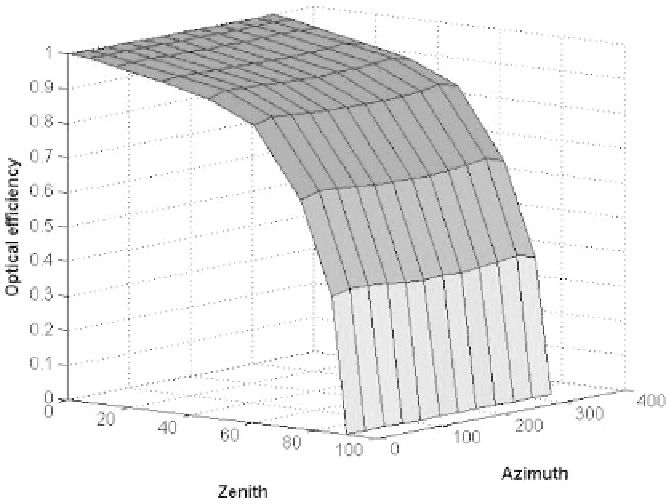
Figure 14.3.18
IAM for PS-10 type central receiver plant.
in Figure 14.3.18: this IAM is taken from the Thermoflex™ database. It can be noted
that the resulting optical efficiency is affected by high zenith angles, while it is almost
constant with the azimuth angle. Single-axis tracking systems are affected by both
angles.
Yearly optical efficiency can be in the range of 61% for a location in France
(Garcia et al., 2008), to 64% for Spain; for comparison, the Spanish case has an
optical efficiency at a nominal operational rate of 77%. As expected, these efficiencies
are higher than linear focus by 10-17%.
14.3.15 Central receiver
Solar radiation is concentrated from heliostats to the central receiver, where it is trans-
ferred to a fluid. There are different types of central receiver: external tubular, cavity
tubular, billboard tubular and volumetric. The central receiver design depends on the
fluid heated and the type of application. For example, volumetric receiver has been
suggested for thermochemical applications at high temperature (Pitz-Paal et al., 2011),
while tubular design is usually applied to water boilers and heat transfer fluid such as
molten salts. This is because in tubular design the high heat transfer coefficient of the
fluid (either water or molten salts) can restrain the temperature of the tube. Conversely,
when a gas fluid is used, the tubular configuration cannot be adopted because of the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search