Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
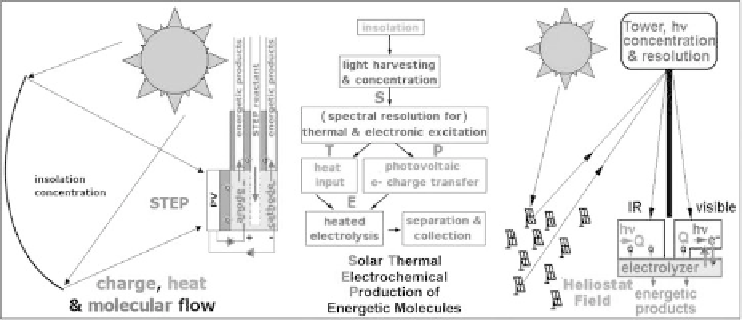
Scheme 8.2.2
Global use of sunlight to drive the formation of energy rich molecules.
Left
: Charge, &
heat flow in
STEP
: heat flow (yellow arrows), electron flow (blue), & reagent flow
(green).
Right
: Beam splitters redirect sub-bandgap sunlight away from the
PV
onto
the electrolyzer. Modified with permission from Licht 2009.
As indicated on the right side of Scheme 8.2.2, the light harvesting can use various opti-
cal configurations; e.g. in lieu of parabolic, or Fresnel, concentrators, a heliostat/solar
tower with secondary optics can achieve higher process temperatures (
>
1000
◦
C) with
concentrations of
2000 suns. Beam splitters can redirect sub-bandgap radiation away
from the PV (minimzing PV heating) for a direct heat exchange with the electrolyzer.
Solar heating can decrease the energy to drive a range of electrolyses. Such pro-
cesses can be determined using available entropy, S, and enthalpy, H, and free-energy,
G, data, (Chase, 1998) and are identified by their negative isothermal temperature
coefficient of the cell potential (deBethune and 1959). This coefficient (dE/dT)
isoth
is
the derivative of the electromotive force of the isothermal cell:
∼
(dE
/
dT)
isoth
=
S
/
nF
=
(
H
−
G)
/
nFT
(8.2.1)
The starting process of modeling any STEP process is the conventional expression of a
generalized electrochemical process, in a cell which drives an n-electron charge transfer
electrolysis reaction, comprising “x'' reactants, R
i
, with stoichiometric coefficients r
i
,
and yielding “y'' products, C
i
, with stoichiometric coefficients c
i
. n-electron refers to
the number of electrons gained to form the cathode products and lost to form the
anode products in the electrolysis reaction.
Electrode 1 | Electrolyte | Electrode 2
Using the convention of E
E
anode
to describe the positive potential neces-
sary to drive a non-spontaneous process, by transfer of n electrons in the electrolysis
reaction:
=
E
cathode
−
y
x
n-electron transfer electrolysis reaction:
r
i
R
i
→
c
i
C
i
(8.2.2)
=
=
i
1
i
1
Search WWH ::

Custom Search