Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
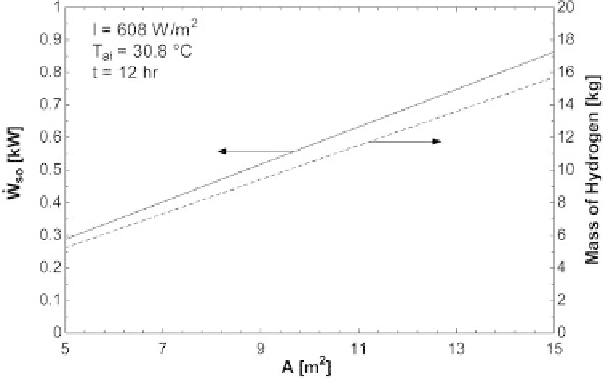
Figure 3.3.13
Effect of increase in area of solar cell on amount of power and hydrogen produced.
Figure 3.3.14
Effect of increase in air inlet temperature on energy and exergy COPs.
and as a result more and more bonds are broken into protons and electrons. As the
power produced by the PV module increases, the hydrogen production rate increases
because more power is being fed into the electrolyzer in order to break the bonds of
water molecules at a higher rate to produce hydrogen. When the water molecules are
broken into hydrogen and oxygen, a greater amount of hydrogen is available which
can be taken out and stored in a cylinder for later use as an energy provider by burning
or using PEMFC.
The effect of an increase in air inlet temperature of energy and exergy COPs of
the TEACS is showing in Figure 3.3.14. The energy and exergy COP are found to be
increasing from 0.95 to 2.51 and 0.89 to 2.36, respectively with increase in air inlet
temperature from 20
◦
Cto40
◦
C. This increase is seen because, as the rate of heat input
to the cooling system decreases to a certain practical limit for achieving certain cooling
load, the performance of the system increases and a lesser amount of heat is being
rejected through condenser.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search