Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
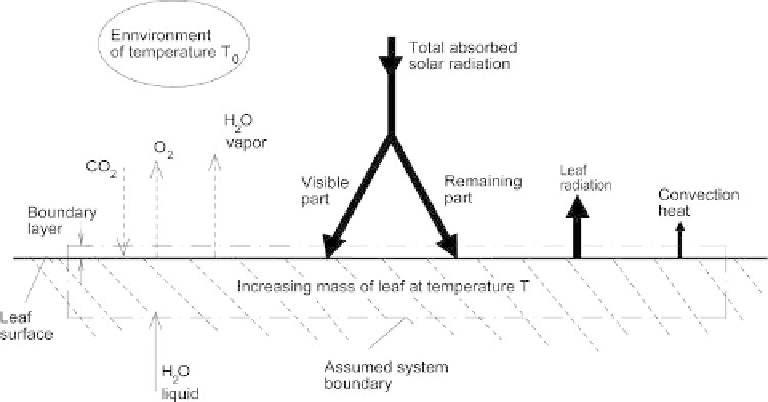
Figure 2.4.19
Simplified scheme of substances and radiation fluxes in photosynthesis, (from Petela,
2008a).
and the matter fluxes observed around the leaf (Figure 2.4.19), are analyzed based on
the following
main assumptions
:
The considered area is a conventional horizontal unitary (1 m
2
) surface of the
leaf in a certain instant at the determined constant conditions during which the
input is equal to output and change in the system.
(i)
(ii)
To determine the actual energy arriving at the leaf surface, the solar radia-
tion energy of the spectrum measured at the highest layer of atmosphere, is
multiplied by a certain weakening factor
γ
; the larger the
γ
, the smaller the
weakening, (
γ
1). In the proposed simplified model the weakening factor is
not studied, nor is it concretely defined. Only certain possible values of
γ
are
used in calculations. The radiation arriving at the leaf could be accurately deter-
mined by measuring of the radiation spectrum directly at the leaf surface so the
factor
γ
would be given. However the purpose of the present considerations is
analysis of photosynthesis for a given
γ
.
≤
(iii)
Cloudy situations are not analyzed.
(iv)
The solar radiation arrives, directly from the Sun in the zenith (solar radiation is
perpendicular to the horizontal surface of the considered leaf), within the solid
angle determined by the diameter of the Sun and its distance from the Earth.
The reduced effect due to the non-perpendicular radiation could be expressed
e.g. by an appropriate value of factor
γ
.
(v)
Sufficient chlorophyll necessary for the photosynthesis process is available.
Any change in the chlorophyll concentration during photosynthesis, and the
thermodynamic effect of such change, are neglected.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search