Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
response of this sensor to the haem saturation (
Sousa, Tuckerman,
Gonzalez, & Gilles-Gonzalez, 2007
).
The crystal structure of the PAS domain of
Sm
FixL has been obtained
only in the deoxy form (
Miyatake et al., 2000
), where for the PAS domain
of
Bj
FixL several conditions originated well-diffracting crystals (
Ayers &
Moffat, 2008; Dunham et al., 2003; Gong et al., 2000, 1998; Hao et al.,
2002; Key & Moffat, 2005
). When comparing the PAS deoxy form of these
sensors, striking similarities are noticed. The haem group is accommodated
in a hydrophobic pocket formed by a long
a
-helix (named F) at the proximal
side that hosts the haem-coordinating histidine residue, and three antiparallel
b
-strands (G, H, and I) at the distal side. The proximal and the distal sides are
covalently linked by a flexible loop between the F and G segments.
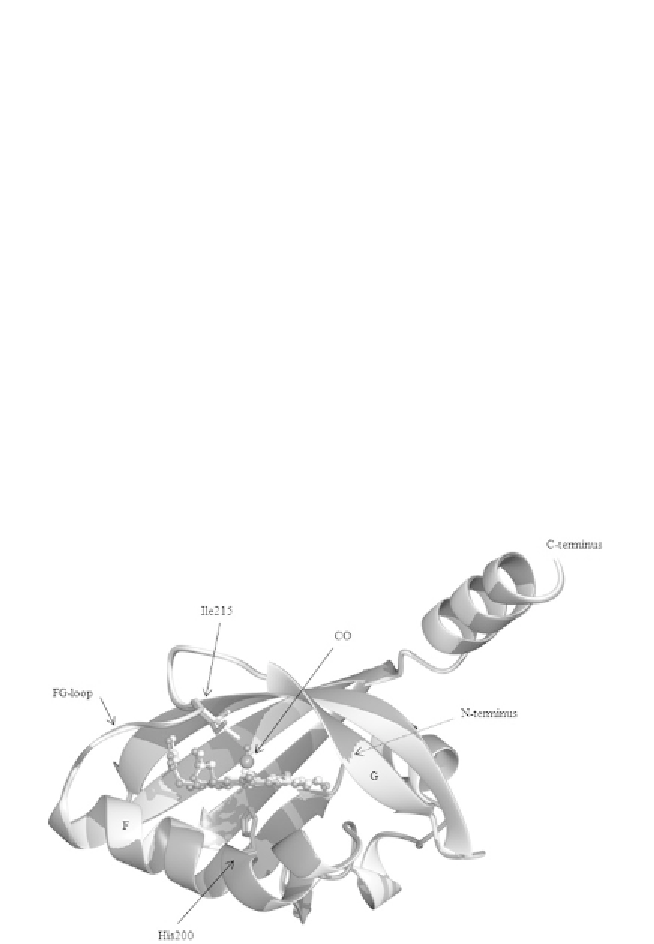
The atomic-resolution structure of
Bj
FixL in the presence of an iron-
bound ligand (e.g. CO and CN
) at the distal side of the haem does
not change significantly the architecture of the pocket, except in the
FG-loop, as described (
Fig. 1.5
). Given the numerous structural affinities
between deoxy-
Sm
FixL and deoxy-
Bj
FixL, it is possible to speculate that
Figure 1.5 Superposition of the BjPAS domain in the unligated (light grey, PDB: 1XJ3)
and in the CO-ligated (dark grey: 1XJ2) form. The haem group (represented in ball-and-
stick) is hosted in a hydrophobic pocket. The two structures are very similar, the main
differences are concentrated in the FG-loop and are probably due to the movement of
Ile215 (Ile209 in SmFixL). Indeed, the presence of CO causes steric repulsion to the Ile215
side chain, which adopts a different conformation.