Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ATP
Glucose
ADP
Glucose-6-phosphate
Fructose-6-phosphate
ATP
ADP
Fructose-1,6-diphosphate
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Diphosphoglyceric acid
ATP
3-phospho-glyceric acid
ADP
2-phospho-glyceric acid
Phosphoenol pyruvic acid
ATP
Pyruvic acid
ADP
FIGURE 6.64
Partial oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid.
activity of microorganisms will be such that only those with negative overall free
energies will proceed spontaneously. Those with positive free energies will need
mediationbyATPandNAD-typecompounds.Aswehaveseen,biochemicalreactions
arethermodynamicallyfeasibleiftheoverallfreeenergychangeisnegative.However,
even if
G
is negative, not all of the reactions will occur at appreciable rates to be of
any use in a living cell. The answer to this is catalysis caused by the
enzymes
present
in all living organisms. In Chapter 5, we derived the rate laws for enzyme catalysis.
In the following section, we will apply those expressions to study reactor design in
environmental engineering.
Δ






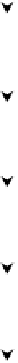








Search WWH ::

Custom Search