Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Upon integration, we obtain
L
o
e
−
k
1
t
,
L
=
(6.81)
where
L
o
is called the
ultimate oxygen demand
for organic matter decomposition.
(Note that there are additional oxygen demands for those compounds that contain
nitrogen, which we will ignore.) The above equation shows that the oxygen demand
decreases exponentially with time. The total oxygen demand of a sample is the sum
of waste consumed in
t
days (BOD
t
) and the oxygen remaining to be used after
t
days. Hence,
L
o
=
BOD
t
+
L
(6.82)
or
e
−
k
1
t
)
.
BOD
t
=
L
o
(
1
−
(6.83)
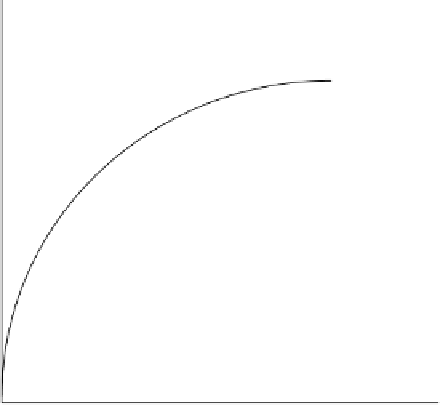
Figure 6.17 represents a typical BOD curve. The value of
k
1
depends on the type of
system under study. Typical values range from 0.05 to 0.3 d
−
1
. Since BOD tests are
carried out at 20
◦
C,
k
1
has to be corrected for other temperatures using the following
equation:
θ
◦
C
)
(k
1
at 20
◦
C
)(
1.047
)
(
θ−
20
)
.
(k
1
at
=
(6.84)
Apart from the BOD, another important and related term used in wastewater
engineering is the
oxygen deficit
,
(expressed in mg/L or kg/m
3
)
, that is defined as
Δ
C
O
2
−
Δ =
C
O
2
,
(6.85)
L
0
L
=
L
0
e
-
k
1
t
)
BOD
t
=
L
0
(1 - e
-
k
1
t
)
Time/days
FIGURE 6.17
A typical BOD curve.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search