Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
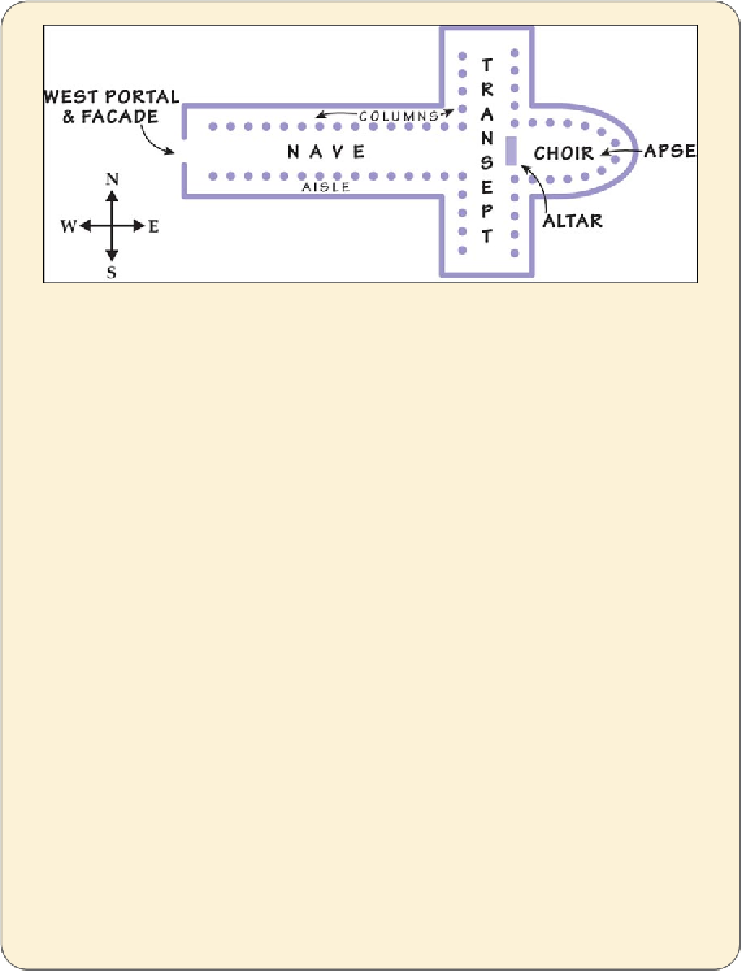
Aisles:
The long, generally low-ceilinged arcades that flank the nave.
Altar:
The raised area with a ceremonial table (often adorned with candles or a cru-
cifix), where the priest prepares and serves the bread and wine for Communion.
Apse:
The space beyond the altar, often bordered with small chapels.
Barrel Vault:
A continuous round-arched ceiling that resembles an extended
upside-down U.
Choir
(“quire” in British English): A cozy area, often screened off, located within
the church nave and near the high altar where services are sung in a more intim-
ate setting.
Cloister:
Covered hallways bordering a square or rectangular open-air courtyard,
traditionally where monks and nuns got fresh air.
Facade:
The exterior surface of the church's main (west) entrance, viewable from
outside and usually highly decorated.
Groin Vault:
An arched ceiling formed where two equal barrel vaults meet at right
angles. Less common usage: term for a medieval jock strap.
Narthex:
The area (portico or foyer) between the main entry and the nave.
Nave:
The long, central section of the church (running west to east, from the en-
trance to the altar) where the congregation sits or stands through the service.
Transept:
In a traditional cross-shaped floor plan, the transept is one of the two
parts forming the “arms” of the cross. The transepts run north-south, perpendic-
ularly crossing the east-west nave.
West Portal:
The main entry to the church (on the west end, opposite the main al-
tar).