Digital Signal Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
0.8τ
1
τ
2
1.2τ
1
frame 2
0.8τ
0
τ
1
1.2τ
0
frame 1
frame 0
τ
min
τ
max
τ
0
(a)
τ
j2
τ
i2
frame 2
τ
j1
frame 1
τ
i1
frame 0
τ
min
τ
j
τ
i
τ
max
(b)
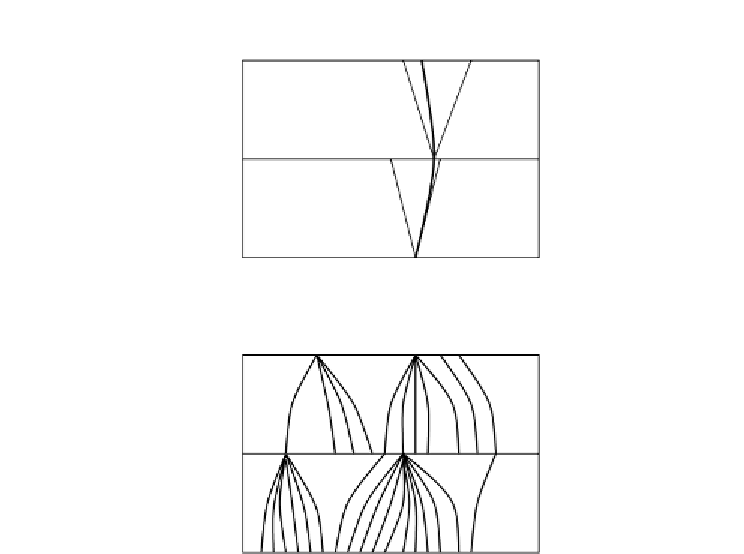
Figure 6.18
Forward pitch tracking: (a) Setting search range limits and (b) Possible
tracked pitch candidates
The active way of using pitch tracking is to apply it at the beginning of
the main processing. Thus, the pitch is not estimated in isolation but by
considering the neighbouring frames. With this pitch-tracking method, the
pitch is estimated as a minimum path error overall. Path error refers to an
accumulated error for a number of adjacent frames, also called the path
penalty. For instance, if a pitch path consists of
τ
0
, τ
1
, τ
2
(see Figure 6.18), the
path penalty is the accumulated error on the path given by:
E
path
=
E
0
(τ
0
)
+
E
1
(τ
1
)
+
E
2
(τ
2
)
(6.35)
where
E
i
(τ
j
)
is the estimated error for candidate
τ
j
in the
i
th
frame. Constraint
conditions must be applied to the possible pitch paths so that the continuity
characteristic can be maintained. Pitch-tracking constraints are as follows:
(
1
−
α)τ
0
≤
τ
1
≤
(
1
+
α)τ
0
(
1
−
α)τ
1
≤
τ
2
≤
(
1
+
α)τ
1
(6.36)


Search WWH ::

Custom Search